Tech
The Crypto Question: Bitcoin, Digital Dollars, and the Future of Money

Introduction
In just over a decade, cryptocurrencies have grown from digital novelties to trillion-dollar technologies with the potential to disrupt the global financial system. An increasing number of investors now hold bitcoin and hundreds of other cryptocurrencies as assets and use them to buy a swath of goods and services, such as software, digital real estate, and illegal drugs.
More From Our Experts
To their proponents, cryptocurrencies are a democratizing force, wresting the power of money creation and control from central banks and Wall Street. Critics, however, say that cryptocurrencies empower criminal groups, terrorist organizations, and rogue states while stoking inequality, suffering from drastic market volatility, and consuming vast amounts of electricity. Regulations vary considerably around the world, with some governments embracing cryptocurrencies and others banning or limiting their use. As of January 2024, 130 countries, including the United States, are considering introducing their own central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) to compete with the cryptocurrency boom.
What are cryptocurrencies?
More on:
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology
So called for their use of cryptography principles to mint virtual coins, cryptocurrencies are typically exchanged on decentralized computer networks between people with virtual wallets. These transactions are recorded publicly on distributed, tamper-proof ledgers known as blockchains. This open-source framework prevents coins from being duplicated and eliminates the need for a central authority such as a bank to validate transactions. Bitcoin, launched in 2009 by the pseudonymous software engineer Satoshi Nakamoto, is by far the most prominent cryptocurrency, and its market capitalization has peaked at more than $1 trillion. Numerous others, including Ethereum, the second-most popular, have proliferated in recent years.
Daily News Brief
A summary of global news developments with CFR analysis delivered to your inbox each morning. Weekdays.
A weekly digest of the latest from CFR on the biggest foreign policy stories of the week, featuring briefs, opinions, and explainers. Every Friday.
A curation of original analyses, data visualizations, and commentaries, examining the debates and efforts to improve health worldwide. Weekly.
By entering your email and clicking subscribe, you’re agreeing to receive announcements from CFR about our products and services, as well as invitations to CFR events. You are also agreeing to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
Cryptocurrency users send funds between digital wallet addresses. These transactions are then recorded into a sequence of numbers known as a “block” and confirmed across the network. Blockchains do not record real names or physical addresses, only the transfers between digital wallets, and thus confer a degree of anonymity on users. Some cryptocurrencies, such as Monero, claim to provide additional privacy. However, if the identity of a wallet owner becomes known, their transactions can be traced.
Bitcoin “miners” earn coins by solving complex math problems to organize these blocks, thereby validating transactions on the network; the process requires a system known as “proof of work.” Many cryptocurrencies use this method, but Ethereum and some others instead use a validation mechanism known as “proof of stake.” In bitcoin’s case, a transaction block is added to the chain every ten minutes, at which point new bitcoin is awarded. (The reward decreases steadily over time.) The total supply of bitcoin is capped at twenty-one million coins, but not all cryptocurrencies have such a constraint.
More From Our Experts
The prices of bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies vary based on global supply and demand. However, the values of some cryptocurrencies are fixed because they are backed by other assets, thus earning them the name “stablecoins.” While these coins tend to claim a peg to a traditional currency, such as $1 per coin, many such currencies were knocked from their pegs during a spate of volatility in 2022.
Why are they popular?
Once dismissed as a fringe interest of tech evangelists, cryptocurrencies—particularly bitcoin—have skyrocketed to mainstream popularity and trillion dollar valuations. In November 2021, the price of bitcoin surged to more than $60,000 for the first time, though it has since fallen. As of mid-2023, an estimated 17 percent of U.S. adults polled by the Pew Research Center had invested in, traded, or used cryptocurrency.
More on:
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology
Different currencies have different appeals, but the popularity of cryptocurrencies largely stems from their decentralized nature: They can be transferred relatively quickly and anonymously, even across borders, without the need for a bank that could block the transaction or charge a fee. Dissidents in authoritarian countries have raised funds in bitcoin to circumvent state controls, including to avoid U.S. sanctions on Russia.
Some analysts say that digital assets are primarily tools for investment. People buy cryptocurrencies “because of a speculative belief that these tokens are going to go up in the future, because a new future is being built on the blockchain,” says CFR Senior Fellow Sebastian Mallaby. Some bitcoin proponents view the cryptocurrency as a hedge against inflation because the supply is permanently fixed, unlike those of fiat currencies, which central banks can expand indefinitely. However, after bitcoin plummeted amid stock market volatility in 2022, many experts questioned this argument. The valuation of other cryptocurrencies can be harder to explain, though many are associated with a larger project within the digital asset industry. Some cryptocurrencies, such as Dogecoin, were created as jokes, but have retained value and garnered investment from high profile investors.
In countries with historically weak currencies, including several Latin American and African countries, bitcoin has become popular with populist leaders. In 2021, El Salvador made waves by becoming the first country to make bitcoin legal tender (residents can pay taxes and settle debts with it), though less than 15 percent of people had used it for that purpose in 2023, according to a poll by Central American University.
The price of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies fluctuates wildly, and some analysts say this limits their usefulness as a means of transaction. (Most buyers and sellers don’t want to accept payment in something whose value can change dramatically from day to day.) Nevertheless, some businesses accept bitcoin.
Experts say stablecoins could be more effective than other cryptocurrencies as a form of payments. The value of stablecoins is, as their names implies, relatively stable, and they can be sent instantly without the transaction fees associated with credit cards or international remittance services such as Western Union. In addition, because stablecoins can be used by anyone with a smartphone, they represent an opportunity to bring millions of people who lack traditional bank accounts into the financial system. However, they have drawn increased scrutiny from regulators, especially after several stablecoins sunk below their $1 pegs during 2022’s market volatility.
What is “DeFi”?
Cryptocurrencies and blockchains have given rise to a new constellation of “decentralized finance” or DeFi businesses and projects. Essentially the cryptocurrency version of Wall Street, DeFi aims to offer people access to financial services—borrowing, lending, and trading—without the need for legacy institutions such as banks and brokerages, which often take large commissions and other fees. Instead, “smart contracts” automatically execute transactions when certain conditions are met.
Most DeFi apps are built on the Ethereum blockchain. Because of its usefulness in tracking transactions, blockchain technology has a range of potential applications beyond cryptocurrency, experts say, such as facilitating international trade [PDF].
“You can imagine a new kind of financial system being constructed out of blockchain-based tokens that have advantages over the old, centralized kinds of money,” says CFR’s Mallaby. “You trust the code, and you trust the blockchain and the decentralized ledger, and it’s a new way of organizing finance.”
What challenges has this created?
Cryptocurrencies have also given rise to a new set of challenges for governments to contend with, including concerns over criminal activity, environmental harms, and consumer protection.
Illicit activities. In recent years, cybercriminals have increasingly carried out ransomware attacks, by which they infiltrate and shut down computer networks and then demand payment to restore them, often in cryptocurrency. Drug cartels and money launderers are also “increasingly incorporating virtual currency” into their activities, according to the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA). U.S. and European authorities have shut down a number of so-called darknet markets—websites where anonymous individuals can use cryptocurrency to buy and sell illegal goods and services, primarily narcotics. Critics say these enforcement efforts have fallen short, exemplified by the theft of more than $1 billion in cryptocurrency by a North Korean hacking group in 2022.
Terrorism and sanctions evasion. The primacy of the U.S. dollar has provided the United States unrivaled power to impose crippling economic sanctions—which states including Iran, North Korea, and Russia are increasingly using cryptocurrency to evade. Meanwhile, terrorist groups such as the self-proclaimed Islamic State, al-Qaeda, and the military wing of the Palestinian organization Hamas also traffic in cryptocurrency.
Environmental harms. Bitcoin mining is an enormously energy-intensive process: the network now consumes more electricity than many countries. This has sparked fears about the cryptocurrency’s contribution to climate change. Cryptocurrency proponents say this problem can be solved using renewable energy; El Salvador’s president has pledged to use volcanic energy to mine bitcoin, for example. Environmental concerns reportedly prompted Ethereum’s move to a proof of stake model, which uses less energy.
Volatility and lack of regulation. The rapid rise of cryptocurrencies and DeFi enterprises means that billions of dollars in transactions are now taking place in a relatively unregulated sector, raising concerns about fraud, tax evasion, and cybersecurity, as well as broader financial stability. If cryptocurrencies become a dominant form of global payments, they could limit the ability of central banks, particularly those in smaller countries, to set monetary policy through control of the money supply.
After high levels of volatility diminished the value of several prominent cryptocurrencies in 2022, a handful of crypto firms were unable to pay back their lenders, which were primarily other crypto firms. Many borrowers and lenders declared bankruptcy, including FTX, at the time the world’s third-largest cryptocurrency exchange. The collapse of FTX and other firms resulted in tens of billions of dollars in losses to investors and led some experts to call for a complete crypto ban, though traditional financial firms were relatively unscathed.
What are governments doing about this?
Many governments have taken a hands-off approach to crypto, but its rapid ascent and evolution, coupled with the rise of DeFi, has forced regulators to begin crafting rules for the emerging sector. Regulations vary widely around the world, with some governments embracing cryptocurrencies and others banning them outright. The challenge for regulators, experts say, is to develop rules that limit traditional financial risks without stifling innovation.
In the United States, policymakers have moved to regulate some cryptocurrencies and the emerging DeFi sector. In January 2024, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved the first set of exchange-traded funds (ETF) that include bitcoin, granting the cryptocurrency entry into the traditional securities market. However, cryptocurrencies do not fit neatly into the existing regulatory framework, creating ambiguity that lawmakers will likely have to resolve. SEC Chairman Gary Gensler has called the cryptocurrency sector a “Wild West,” and compared it to the 1920s, before the United States had securities laws; he has urged Congress to give the SEC greater oversight over bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell and Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen have both called for stronger regulations of stablecoins. But regulators have thus far been reluctant to extend crypto investors the same protections that exist in more traditional finance, such as deposit insurance. “If you buy crypto-assets and the price goes to zero at some point, please don’t be surprised and don’t expect taxpayers to socialize your losses,” the Federal Reserve Board of Governors’ Christopher J. Waller said in 2023.
To limit illicit activities, authorities have targeted the exchanges that allow users to convert cryptocurrencies to U.S. dollars and other national currencies. Under pressure from regulators, major exchanges including Coinbase and Gemini adhere to “know your customer” and other anti–money laundering requirements. Law enforcement and intelligence agencies, meanwhile, are learning to leverage the traceability of most cryptocurrencies by using blockchains to analyze and track criminal activity. For example, some of the ransom paid to the Colonial Pipeline hackers was later recovered by the FBI. In August 2022, the Treasury Department announced a crackdown on so-called cryptocurrency mixers that criminals can use to anonymize transactions on the blockchain, calling them a “threat to U.S. national security.”
China, which accounts for most of the world’s bitcoin mining, has moved aggressively to crack down on cryptocurrencies. In September 2021, Chinese authorities announced a sweeping ban on all crypto transactions and mining, causing the price of some cryptocurrencies to fall sharply in the immediate aftermath. According to the Atlantic Council, at least eight other countries (Algeria, Bangladesh, Bolivia, Morocco, Nepal, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and Tunisia) have banned cryptocurrencies, while dozens more have sought to restrict adoption of digital assets. However, such restrictions are hard to enforce, and crypto exchanges have generated tens of billions in revenue from countries with cryptocurrency bans. Meanwhile, most other governments have so far taken a relatively limited approach.
What is a central bank digital currency?
In an effort to assert sovereignty, many central banks, including the U.S. Federal Reserve, are considering introducing their own digital cash, known as a central bank digital currency (CBDC). For proponents, CBDCs promise the speed and other benefits of cryptocurrency without the associated risks. Scores of countries—together representing more than 98 percent of the global economy—are exploring CBDCs. Eleven countries have fully launched CBDCs. All are lower-income and ten are in the Caribbean (Nigeria is the eleventh). In 2023, China began counting its piloted CBDC in official currency circulation calculations, though the digital yuan represented just 0.1 percent of central bank cash and reserves. In the United States, there is reportedly disagreement among Fed officials over the need for a digital dollar.
One way to implement CBDCs would be for citizens to have accounts directly with the central bank [PDF]. This would give governments powerful new ways of managing the economy—stimulus payments and other benefits could be credited to people directly, for example—and the central bank’s imprimatur would make CBDCs a safe digital asset to hold. But their introduction could also create new problems, experts say, by centralizing an enormous amount of power, data, and risk within a single bank and potentially compromising privacy and cybersecurity.
Some experts say the potential for CBDCs to cut out commercial banks as intermediaries carries risks, because these banks perform a critical economic role by creating and allocating credit (i.e., making loans). If people chose to bank directly with the Fed, that would require the central bank to either facilitate consumer borrowing, which it might not be equipped to do, or find new ways of injecting credit. For these reasons, some experts say private, regulated digital currencies are preferable to CBDCs.
Tech
Harvard Alumni, Tech Moguls, and Best-Selling Authors Drive Nearly $600 Million in Pre-Order Sales

BlockDAG Network’s history is one of innovation, perseverance, and a vision to push the boundaries of blockchain technology. With Harvard alumni, tech moguls, and best-selling authors at the helm, BlockDAG is rewriting the rules of the cryptocurrency game.
CEO Antony Turner, inspired by the successes and shortcomings of Bitcoin and Ethereum, says, “BlockDAG leverages existing technology to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.” This powerhouse team has led a staggering 1,600% price increase in 20 pre-sale rounds, raising over $63.9 million. The secret? Unparalleled expertise and a bold vision for the future of blockchain.
Let’s dive into BlockDAG’s success story and find out what the future holds for this cryptocurrency.
The Origin: Why BlockDAG Was Created
In a recent interview, BlockDAG CEO Antony Turner perfectly summed up why the market needs BlockDAG’s ongoing revolution. He said:
“The creation of BlockDAG was inspired by Bitcoin and Ethereum, their successes and their shortcomings.
If you look at almost any new technology, it is very rare that the first movers remain at the forefront forever. Later incumbents have a huge advantage in entering a market where the need has been established and the technology is no longer cutting edge.
BlockDAG has done just that: our innovation is incorporating existing technology to provide a better solution, allowing us to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.”
The Present: How Far Has BlockDAG Come?
BlockDAG’s presale is setting new benchmarks in the cryptocurrency investment landscape. With a stunning 1600% price increase over 20 presale lots, it has already raised over $63.9 million in capital, having sold over 12.43 billion BDAG coins.
This impressive performance underscores the overwhelming confidence of investors in BlockDAG’s vision and leadership. The presale attracted over 20,000 individual investors, with the BlockDAG community growing exponentially by the hour.

These monumental milestones have been achieved thanks to the unparalleled skills, experience and expertise of BlockDAG’s management team:
Antony Turner – Chief Executive Officer
Antony Turner, CEO of BlockDAG, has over 20 years of experience in the Fintech, EdTech, Travel and Crypto industries. He has held senior roles at SPIRIT Blockchain Capital and co-founded Axona-Analytics and SwissOne. Antony excels in financial modeling, business management and scaling growth companies, with expertise in trading, software, IoT, blockchain and cryptocurrency.
Director of Communications
Youssef Khaoulaj, CSO of BlockDAG, is a Smart Contract Auditor, Metaverse Expert, and Red Team Hacker. He ensures system security and disaster preparedness, and advises senior management on security issues.
advisory Committee
Steven Clarke-Martin, a technologist and consultant, excels in enterprise technology, startups, and blockchain, with a focus on DAOs and smart contracts. Maurice Herlihy, a Harvard and MIT graduate, is an award-winning computer scientist at Brown University, with experience in distributed computing and consulting roles, most notably at Algorand.
The Future: Becoming the Cryptocurrency with the Highest Market Cap in the World
Given its impressive track record and a team of geniuses working tirelessly behind the scenes, BlockDAG is quickly approaching the $600 million pre-sale milestone. This crypto powerhouse will soon enter the top 30 cryptocurrencies by market cap.
Currently trading at $0.017 per coin, BlockDAG is expected to hit $1 million in the coming months, with the potential to hit $30 per coin by 2030. Early investors have already enjoyed a 1600% ROI by batch 21, fueling a huge amount of excitement around BlockDAG’s presale. The platform is seeing significant whale buying, and demand is so high that batch 21 is almost sold out. The upcoming batch is expected to drive prices even higher.

Invest in BlockDAG Pre-Sale Now:
Pre-sale: https://purchase.blockdag.network
Website: https://blockdag.network
Telegram: https://t.me/blockDAGnetwork
Discord: Italian: https://discord.gg/Q7BxghMVyu
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
How Karak’s Latest Tech Integration Could Make Data Breaches Obsolete

- Space and Time uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure secure and tamper-proof data processing for smart contracts and enterprises.
- The integration facilitates faster development and deployment of Distributed Secure Services (DSS) on the Karak platform.
Karak, a platform known for its strong security capabilities, is enhancing its Distributed Secure Services (DSS) by integrating Space and Time as a zero-knowledge (ZK) coprocessor. This move is intended to strengthen trustless operations across its network, especially in slashing and rewards mechanisms.
Space and Time is a verifiable processing layer that uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure that computations on decentralized data warehouses are secure and untampered with. This system enables smart contracts, large language models (LLMs), and enterprises to process data without integrity concerns.
The integration with Karak will enable the platform to use Proof of SQL, a new ZK-proof approach developed by Space and Time, to confirm that SQL query results are accurate and have not been tampered with.
One of the key features of this integration is the enhancement of DSS on Karak. DSS are decentralized services that use re-staked assets to secure the various operations they provide, from simple utilities to complex marketplaces. The addition of Space and Time technology enables faster development and deployment of these services, especially by simplifying slashing logic, which is critical to maintaining security and trust in decentralized networks.
Additionally, Space and Time is developing its own DSS for blockchain data indexing. This service will allow community members to easily participate in the network by running indexing nodes. This is especially beneficial for applications that require high security and decentralization, such as decentralized data indexing.
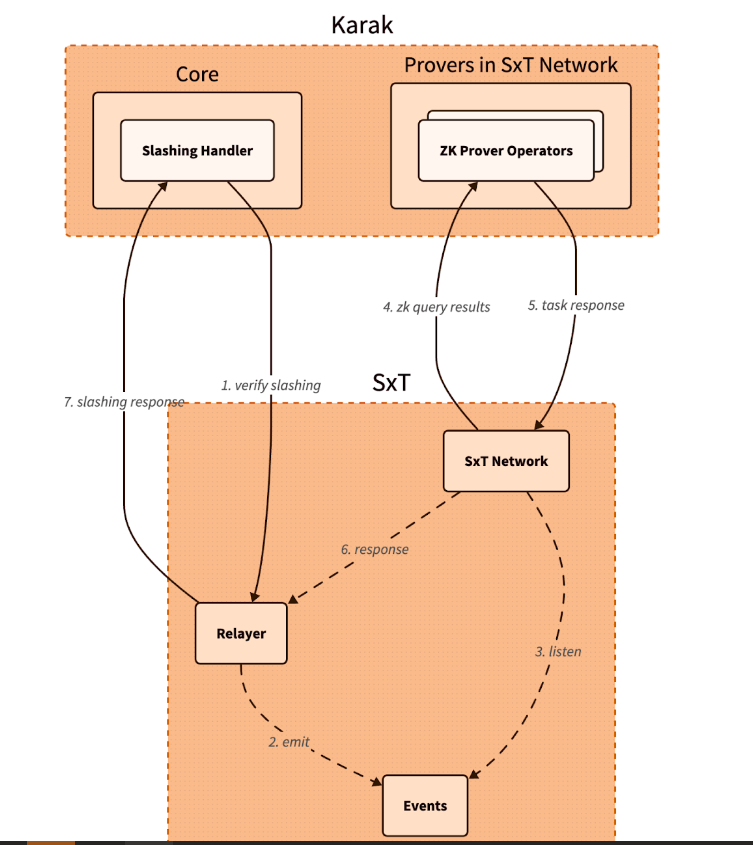
The integration architecture follows a detailed and secure flow. When a Karak slashing contract needs to verify a SQL query, it calls the Space and Time relayer contract with the required SQL statement. This contract then emits an event with the query details, which is detected by operators in the Space and Time network.
These operators, responsible for indexing and monitoring DSS activities, validate the event and route the work to a verification operator who runs the query and generates the necessary ZK proof.
The result, along with a cryptographic commitment on the queried data, is sent to the relayer contract, which verifies and returns the data to the Karak cutter contract. This end-to-end process ensures that the data used in decision-making, such as determining penalties within the DSS, is accurate and reliable.
Karak’s mission is to provide universal security, but it also extends the capabilities of Space and Time to support multiple DSSs with their data indexing needs. As these technologies evolve, they are set to redefine the secure, decentralized computing landscape, making it more accessible and efficient for developers and enterprises alike. This integration represents a significant step towards a more secure and verifiable digital infrastructure in the blockchain space.
Website | X (Twitter) | Discord | Telegram
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
Cryptocurrency Payments: Should CFOs Consider This Ferrari-Approved Trend?

Iconic Italian luxury carmaker Ferrari has announced the expansion of its cryptocurrency payment system to its European dealer network.
The move, which follows a successful launch in North America less than a year ago, raises a crucial question for CFOs across industries: Is it time to consider accepting cryptocurrency as a form of payment for your business?
Ferrari’s move isn’t an isolated one. It’s part of a broader trend of companies embracing digital assets. As of 2024, we’re seeing a growing number of companies, from tech giants to traditional retailers, accepting cryptocurrencies.
This change is determined by several factors:
- Growing mainstream adoption of cryptocurrencies
- Growing demand from tech-savvy and affluent consumers
- Potential for faster and cheaper international transactions
- Desire to project an innovative brand image
Ferrari’s approach is particularly noteworthy. They have partnered with BitPay, a leading cryptocurrency payment processor, to allow customers to purchase vehicles using Bitcoin, Ethereum, and USDC. This satisfies their tech-savvy and affluent customer base, many of whom have large digital asset holdings.
Navigating Opportunities and Challenges
Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments illustrates several key opportunities for companies considering this move. First, it opens the door to new customer segments. By accepting cryptocurrency, Ferrari is targeting a younger, tech-savvy demographic—people who have embraced digital assets and see them as a legitimate form of value exchange. This strategy allows the company to connect with a new generation of affluent customers who may prefer to conduct high-value transactions in cryptocurrency.
Second, cryptocurrency adoption increases global reach. International payments, which can be complex and time-consuming with traditional methods, become significantly easier with cryptocurrency transactions. This can be especially beneficial for businesses that operate in multiple countries or deal with international customers, as it potentially reduces friction in cross-border transactions.
Third, accepting cryptocurrency positions a company as innovative and forward-thinking. In today’s fast-paced business environment, being seen as an early adopter of emerging technologies can significantly boost a brand’s image. Ferrari’s move sends a clear message that they are at the forefront of financial innovation, which can appeal to customers who value cutting-edge approaches.
Finally, there is the potential for cost savings. Traditional payment methods, especially for international transactions, often incur substantial fees. Cryptocurrency transactions, on the other hand, can offer lower transaction costs. For high-value purchases, such as luxury cars, these savings could be significant for both the business and the customer.
While the opportunities are enticing, accepting cryptocurrency payments also presents significant challenges that businesses must address. The most notable of these is volatility. Cryptocurrency values can fluctuate dramatically, sometimes within hours, posing potential risk to businesses that accept them as payment. Ferrari addressed this challenge by implementing a system that instantly converts cryptocurrency received into traditional fiat currencies, effectively mitigating the risk of value fluctuations.
Regulatory uncertainty is another major concern. The legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies is still evolving in many jurisdictions around the world. This lack of clear and consistent regulations can create compliance challenges for companies, especially those operating internationally. Companies must remain vigilant and adaptable as new laws and regulations emerge, which can be a resource-intensive process.
Implementation costs are also a significant obstacle. Integrating cryptocurrency payment systems often requires substantial investment in new technology infrastructure and extensive staff training. This can be especially challenging for small businesses or those with limited IT resources. The costs are not just financial; a significant investment of time is also required to ensure smooth implementation and operation.
Finally, security concerns loom large in the world of cryptocurrency transactions. While blockchain technology offers some security benefits, cryptocurrency transactions still require robust cybersecurity measures to protect against fraud, hacks, and other malicious activity. Businesses must invest in robust security protocols and stay up-to-date on the latest threats and protections, adding another layer of complexity and potential costs to accepting cryptocurrency payments.
Strategic Considerations for CFOs
If you’re thinking of following in Ferrari’s footsteps, here are the key factors to consider:
- Risk Assessment: Carefully evaluate potential risks to your business, including financial, regulatory, and reputational risks.
- Market Analysis: Evaluate whether your customer base is significantly interested in using cryptocurrencies for payments.
- Technology Infrastructure: Determine the costs and complexities of implementing a cryptographic payment system that integrates with existing financial processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that cryptocurrency acceptance is in line with local regulations in all markets you operate in. Ferrari’s gradual rollout demonstrates the importance of this consideration.
- Financial Impact: Analyze how accepting cryptocurrency could impact your cash flow, accounting practices, and financial reporting.
- Partnership Evaluation: Consider partnering with established crypto payment processors to reduce risk and simplify implementation.
- Employee Training: Plan comprehensive training to ensure your team is equipped to handle cryptocurrency transactions and answer customer questions.
While Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments is exciting, it’s important to consider this trend carefully.
A CFO’s decision to adopt cryptocurrency as a means of payment should be based on a thorough analysis of your company’s specific needs, risk tolerance, and strategic goals. Cryptocurrency payments may not be right for every business, but for some, they could provide a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Remember that the landscape is rapidly evolving. Stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. Whether you decide to accelerate your crypto engines now or wait in the pit, keeping this payment option on your radar is critical to navigating the future of business transactions.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
Sign up to receive your daily business insights
Tech
Bitcoin Tumbles as Crypto Market Selloff Mirrors Tech Stocks’ Plunge
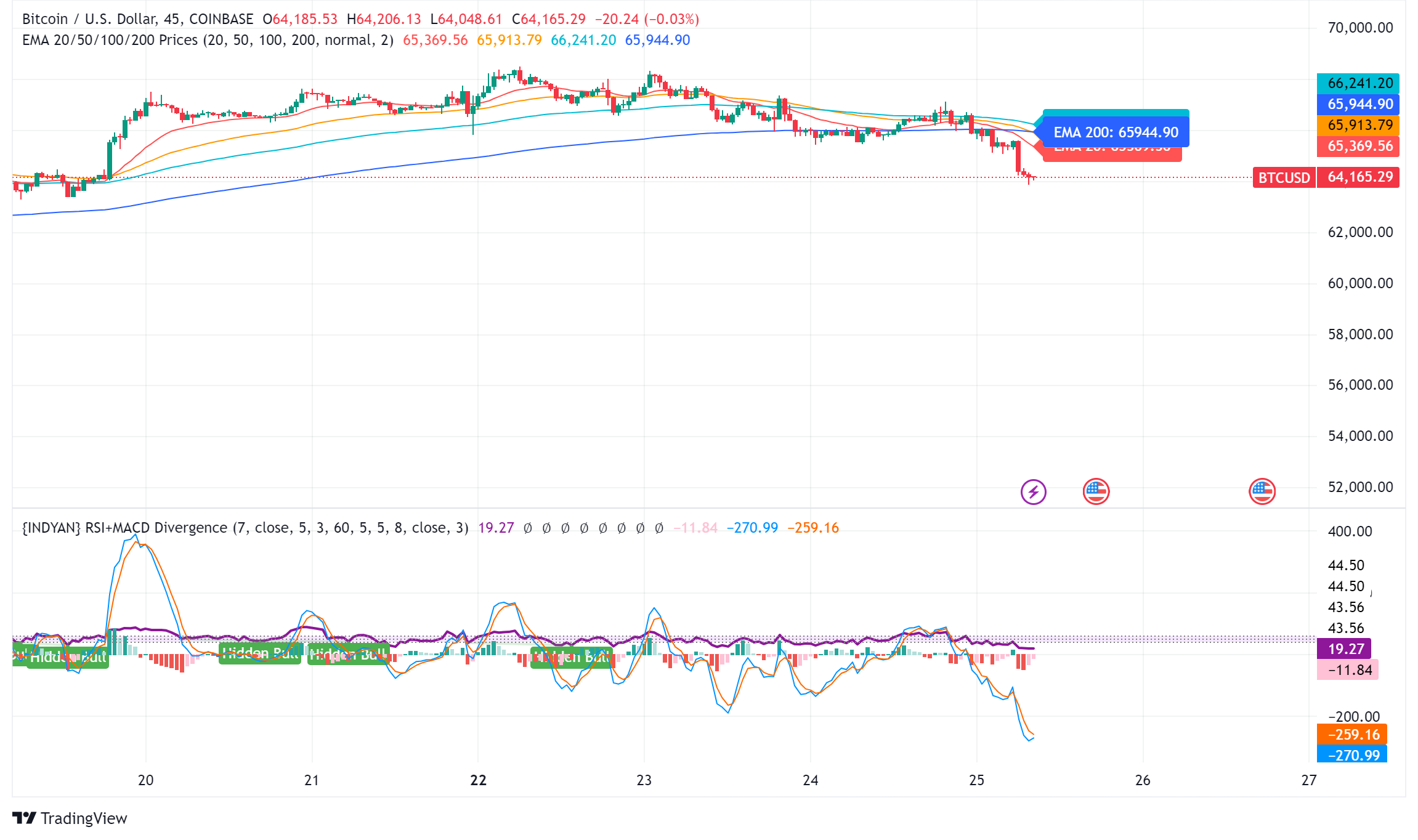
The world’s largest cryptocurrency, Bitcoin (BTC), suffered a significant price decline on Wednesday, falling below $65,000. The decline coincides with a broader market sell-off that has hit technology stocks hard.
Cryptocurrency Liquidations Hit Hard
CoinGlass data reveals a surge in long liquidations in the cryptocurrency market over the past 24 hours. These liquidations, totaling $220.7 million, represent forced selling of positions that had bet on price increases. Bitcoin itself accounted for $14.8 million in long liquidations.
Ethereum leads the decline
Ethereal (ETH), the second-largest cryptocurrency, has seen a steeper decline than Bitcoin, falling nearly 8% to trade around $3,177. This decline mirrors Bitcoin’s price action, suggesting a broader market correction.
Cryptocurrency market crash mirrors tech sector crash
The cryptocurrency market decline appears to be linked to the significant losses seen in the U.S. stock market on Wednesday. Stock market listing The index, heavily weighted toward technology stocks, posted its sharpest decline since October 2022, falling 3.65%.
Analysts cite multiple factors
Several factors may have contributed to the cryptocurrency market crash:
- Tech earnings are underwhelming: Earnings reports from tech giants like Alphabet are disappointing (Google(the parent company of), on Tuesday, triggered a sell-off in technology stocks with higher-than-expected capital expenditures that could have repercussions on the cryptocurrency market.
- Changing Political Landscape: The potential impact of the upcoming US elections and changes in Washington’s policy stance towards cryptocurrencies could influence investor sentiment.
- Ethereal ETF Hopes on the line: While bullish sentiment around a potential U.S. Ethereum ETF initially boosted the market, delays or rejections could dampen enthusiasm.
Analysts’ opinions differ
Despite the short-term losses, some analysts remain optimistic about Bitcoin’s long-term prospects. Singapore-based cryptocurrency trading firm QCP Capital believes Bitcoin could follow a similar trajectory to its post-ETF launch all-time high, with Ethereum potentially converging with its previous highs on sustained institutional interest.
Rich Dad Poor Dad Author’s Prediction
Robert Kiyosaki, author of the best-selling Rich Dad Poor Dad, predicts a potential surge in the price of Bitcoin if Donald Trump is re-elected as US president. He predicts a surge to $105,000 per coin by August 2025, fueled by a weaker dollar that is set to boost US exports.
BTC/USD Technical Outlook
Bitcoin price is currently trading below key support levels, including the $65,500 level and the 100 hourly moving average. A break below the $64,000 level could lead to further declines towards the $63,200 support zone. However, a recovery above the $65,500 level could trigger another increase in the coming sessions.
-

 Videos4 weeks ago
Videos4 weeks agoAbsolutely massive: the next higher Bitcoin leg will shatter all expectations – Tom Lee
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoVolta Finance Limited – Director/PDMR Shareholding
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoModiv Industrial to release Q2 2024 financial results on August 6
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoApple to report third-quarter earnings as Wall Street eyes China sales
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoNumber of Americans filing for unemployment benefits hits highest level in a year
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoInventiva reports 2024 First Quarter Financial Information¹ and provides a corporate update
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoLeeds hospitals trust says finances are “critical” amid £110m deficit
-

 Markets1 year ago
Markets1 year agoWhale Investments in Bitcoin Hit $100 Billion in 2024, Fueling Insane Investor Optimism ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 DeFi1 year ago
DeFi1 year ago🏴☠️ Pump.Fun operated by Insider Exploit
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year ago$1,000,000 worth of BTC in 2025! Get ready for an UNPRECEDENTED PRICE EXPLOSION – Jack Mallers
-
 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoABSOLUTELY HUGE: Bitcoin is poised for unabated exponential growth – Mark Yusko and Willy Woo
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoBlockDAG ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Review: Is It the Next Big Thing in Cryptocurrency? 5 questions answered

















