Tech
What is Blockchain Technology? How Does Blockchain Work? [Updated]
![What is Blockchain Technology? How Does Blockchain Work? [Updated]](https://digitalfinancenews.life/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/1720528807_What-is-Blockchain-Technology-How-Does-Blockchain-Work-Updated.png)
Reviewed and fact-checked by Sayantoni Das
Over the past few years, you have consistently heard the term ‘blockchain technology,’ probably regarding cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin. In fact, you may be asking yourself, “what is blockchain technology?” It seems like blockchain is a platitude but in a hypothetical sense, as there is no real meaning that the layman can understand easily. It is imperative to answer “what is blockchain technology, “including the technology that is used, how it works, and how it’s becoming vital in the digital world.
As blockchain continues to grow and become more user-friendly, the onus is on you to learn this evolving technology to prepare for the future. If you are new to blockchain, then this is the right platform to gain solid foundational knowledge. In this article, you learn how to answer the question, “what is blockchain technology?” You’ll also learn how blockchain works, why it’s important, and how you can use this field to advance your career.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a method of recording information that makes it impossible or difficult for the system to be changed, hacked, or manipulated. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that duplicates and distributes transactions across the network of computers participating in the blockchain.
Blockchain technology is a structure that stores transactional records, also known as the block, of the public in several databases, known as the “chain,” in a network connected through peer-to-peer nodes. Typically, this storage is referred to as a ‘digital ledger.’
Every transaction in this ledger is authorized by the digital signature of the owner, which authenticates the transaction and safeguards it from tampering. Hence, the information the digital ledger contains is highly secure.
In simpler words, the digital ledger is like a Google spreadsheet shared among numerous computers in a network, in which, the transactional records are stored based on actual purchases. The fascinating angle is that anybody can see the data, but they can’t corrupt it.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program
Dive into the transformative world of blockchain technology with our intensive Cyber security Bootcamp. Uncover the revolutionary potential of blockchain while honing your skills in safeguarding these decentralized systems. From understanding the intricacies of smart contracts to fortifying digital transactions, this bootcamp equips you to navigate the evolving landscape of cybersecurity within the blockchain domain. Don’t miss this opportunity to become a proficient cybersecurity professional in the realm of blockchain.
Why is Blockchain Popular?
Suppose you are transferring money to your family or friends from your bank account. You would log in to online banking and transfer the amount to the other person using their account number. When the transaction is done, your bank updates the transaction records. It seems simple enough, right? There is a potential issue which most of us neglect.
These types of transactions can be tampered with very quickly. People who are familiar with this truth are often wary of using these types of transactions, hence the evolution of third-party payment applications in recent years. But this vulnerability is essentially why Blockchain technology was created.
Technologically, Blockchain is a digital ledger that is gaining a lot of attention and traction recently. But why has it become so popular? Well, let’s dig into it to fathom the whole concept.
Record keeping of data and transactions are a crucial part of the business. Often, this information is handled in house or passed through a third party like brokers, bankers, or lawyers increasing time, cost, or both on the business. Fortunately, Blockchain avoids this long process and facilitates the faster movement of the transaction, thereby saving both time and money.
Most people assume Blockchain and Bitcoin can be used interchangeably, but in reality, that’s not the case. Blockchain is the technology capable of supporting various applications related to multiple industries like finance, supply chain, manufacturing, etc., but Bitcoin is a currency that relies on Blockchain technology to be secure.
Blockchain is an emerging technology with many advantages in an increasingly digital world:
-
Highly Secure
It uses a digital signature feature to conduct fraud-free transactions making it impossible to corrupt or change the data of an individual by the other users without a specific digital signature.
-
Decentralized System
Conventionally, you need the approval of regulatory authorities like a government or bank for transactions; however, with Blockchain, transactions are done with the mutual consensus of users resulting in smoother, safer, and faster transactions.
-
Automation Capability
It is programmable and can generate systematic actions, events, and payments automatically when the criteria of the trigger are met.
Structure and Design of Blockchain
A blockchain is a distributed, immutable, and decentralized ledger at its core that consists of a chain of blocks and each block contains a set of data. The blocks are linked together using cryptographic techniques and form a chronological chain of information. The structure of a blockchain is designed to ensure the security of data through its consensus mechanism which has a network of nodes that agree on the validity of transactions before adding them to the blockchain.
Blocks:
A block in a blockchain is a combination of three main components:
1. The header contains metadata such as a timestamp which has a random number used in the mining process and the previous block’s hash.
2. The data section contains the main and actual information like transactions and smart contracts which are stored in the block.
3. Lastly, the hash is a unique cryptographic value that works as a representative of the entire block which is used for verification purposes.
Block Time:
Block time refers to the time taken to generate a new block in a blockchain. Different blockchains have different block times, which can vary from a few seconds to minutes or may be in hours too. Shorter block times can give faster transaction confirmations but the result has higher chances of conflicts but the longer block times may increase the timing for transaction confirmations but reduce the chances of conflicts.
Hard Forks:
A hard fork in a blockchain refers to a permanent divergence in the blockchain’s history that results in two separate chains. It can happen due to a fundamental change in the protocol of a blockchain and all nodes do not agree on the update. Hard forks can create new cryptocurrencies or the splitting of existing ones and It requires consensus among the network participants to resolve.
Decentralization:
Decentralization is the key feature of blockchain technology. In a decentralized blockchain, there is no single central authority that can control the network. In decentralization,the decision-making power is distributed among a network of nodes that collectively validate and agree on the transactions to be added to the blockchain. This decentralized nature of blockchain technology helps to promote transparency, trust, and security. It also reduces the risk to rely on a single point of failure and minimizes the risks of data manipulation.
Finality:
Finality refers to the irreversible confirmation of transactions in a blockchain. If and when a transaction is added to a block and the block is confirmed by the network, it becomes immutable and cannot be reversed. This feature ensures the integrity of the data and prevents double spending, providing a high level of security and trust in Blockchain Types & Sustainability
Openness:
Openness in blockchain technology makes the blockchain accessible to anyone who intends to participate in the network. This implies that it is open for all and anyone can join the network, validate transactions, and can add new blocks to the blockchain, so long as they know the consensus rules. Openness promotes inclusivity, transparency, and innovation, as it allows for participation from various stakeholders.
Public Blockchain:
It is a kind of blockchain which is open for the public and allows everyone to join the network to perform transactions and to participate in the consensus process. Public blockchains are transparent, because all transactions are publicly recorded.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
In recent years, you may have noticed many businesses around the world integrating Blockchain technology. But how exactly does Blockchain technology work? Is this a significant change or a simple addition? The advancements of Blockchain are still young and have the potential to be revolutionary in the future; so, let’s begin demystifying this technology.
Blockchain is a combination of three leading technologies:
- Cryptographic keys
- A peer-to-peer network containing a shared ledger
- A means of computing, to store the transactions and records of the network
Cryptography keys consist of two keys – Private key and Public key. These keys help in performing successful transactions between two parties. Each individual has these two keys, which they use to produce a secure digital identity reference. This secured identity is the most important aspect of Blockchain technology. In the world of cryptocurrency, this identity is referred to as ‘digital signature’ and is used for authorizing and controlling transactions.
The digital signature is merged with the peer-to-peer network; a large number of individuals who act as authorities use the digital signature in order to reach a consensus on transactions, among other issues. When they authorize a deal, it is certified by a mathematical verification, which results in a successful secured transaction between the two network-connected parties. So to sum it up, Blockchain users employ cryptography keys to perform different types of digital interactions over the peer-to-peer network.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
Types of Blockchain
There are different types of blockchains. They are as follows:
Private Blockchain Networks
Private blockchains operate on closed networks, and tend to work well for private businesses and organizations. Companies can use private blockchains to customize their accessibility and authorization preferences, parameters to the network, and other important security options. Only one authority manages a private blockchain network.
Public Blockchain Networks
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies originated from public blockchains, which also played a role in popularizing distributed ledger technology (DLT). Public blockchains also help to eliminate certain challenges and issues, such as security flaws and centralization. With DLT, data is distributed across a peer-to-peer network, rather than being stored in a single location. A consensus algorithm is used for verifying information authenticity; proof of stake (PoS) and proof of work (PoW) are two frequently used consensus methods.
Permissioned Blockchain Networks
Also sometimes known as hybrid blockchains, permissioned blockchain networks are private blockchains that allow special access for authorized individuals. Organizations typically set up these types of blockchains to get the best of both worlds, and it enables better structure when assigning who can participate in the network and in what transactions.
Consortium Blockchains
Similar to permissioned blockchains, consortium blockchains have both public and private components, except multiple organizations will manage a single consortium blockchain network. Although these types of blockchains can initially be more complex to set up, once they are running, they can offer better security. Additionally, consortium blockchains are optimal for collaboration with multiple organizations.
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains are the combination of both public and private blockchains. In a hybrid blockchain, some parts of the blockchain are public and transparent, while others are private and accessible only to authorized and specific participants. This makes hybrid blockchains ideal for use in those cases where a balance is required between transparency and privacy. For example, in supply chain management multiple parties can access certain information, but sensitive data can be kept private.
Sidechains
Sidechains are different blockchains that run parallel to the main blockchain, allowing for additional functionality and scalability. Sidechains enable developers to experiment with new features and applications without affecting the main blockchain’s integrity. For example, sidechains can be used for creating decentralized applications and to implement specific consensus mechanisms. Sidechains can also be used to handle transactions of the main blockchain to reduce congestion and increase scalability.
Blockchain Layers
Blockchain layers refer to the concept of building multiple layers of blockchains on top of each other. Each layer can have its own consensus mechanism, rules, and functionality which can interact with other layers. This ensures greater scalability, as transactions can be processed in parallel across different layers. For example, the Lightning Network, built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, is a second layer solution that enables faster and cheaper transactions by creating payment channels between users.
The Process of Transaction
One of Blockchain technology’s cardinal features is the way it confirms and authorizes transactions. For example, if two individuals wish to perform a transaction with a private and public key, respectively, the first person party would attach the transaction information to the public key of the second party. This total information is gathered together into a block.
The block contains a digital signature, a timestamp, and other important, relevant information. It should be noted that the block doesn’t include the identities of the individuals involved in the transaction. This block is then transmitted across all of the network’s nodes, and when the right individual uses his private key and matches it with the block, the transaction gets completed successfully.
In addition to conducting financial transactions, the Blockchain can also hold transactional details of properties, vehicles, etc.
Here’s a use case that illustrates how Blockchain works:
-
Hash Encryptions
blockchain technology uses hashing and encryption to secure the data, relying mainly on the SHA256 algorithm to secure the information. The address of the sender (public key), the receiver’s address, the transaction, and his/her private key details are transmitted via the SHA256 algorithm. The encrypted information, called hash encryption, is transmitted across the world and added to the blockchain after verification. The SHA256 algorithm makes it almost impossible to hack the hash encryption, which in turn simplifies the sender and receiver’s authentication.
-
Proof of Work
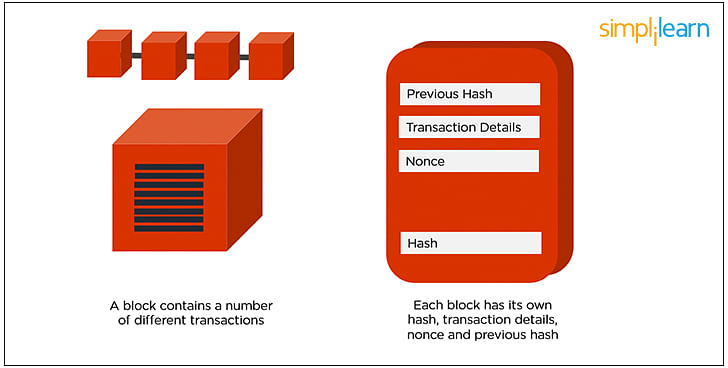
In a Blockchain, each block consists of 4 main headers.
- Previous Hash: This hash address locates the previous block.
- Transaction Details: Details of all the transactions that need to occur.
- Nonce: An arbitrary number given in cryptography to differentiate the block’s hash address.
- Hash Address of the Block: All of the above (i.e., preceding hash, transaction details, and nonce) are transmitted through a hashing algorithm. This gives an output containing a 256-bit, 64 character length value, which is called the unique ‘hash address.’ Consequently, it is referred to as the hash of the block.
- Numerous people around the world try to figure out the right hash value to meet a pre-determined condition using computational algorithms. The transaction completes when the predetermined condition is met. To put it more plainly, Blockchain miners attempt to solve a mathematical puzzle, which is referred to as a proof of work problem. Whoever solves it first gets a reward.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
-
Mining
In Blockchain technology, the process of adding transactional details to the present digital/public ledger is called ‘mining.’ Though the term is associated with Bitcoin, it is used to refer to other Blockchain technologies as well. Mining involves generating the hash of a block transaction, which is tough to forge, thereby ensuring the safety of the entire Blockchain without needing a central system.
History of Blockchain
Satoshi Nakamoto, whose real identity still remains unknown to date, first introduced the concept of blockchains in 2008. The design continued to improve and evolve, with Nakamoto using a Hashcash-like method. It eventually became a primary component of bitcoin, a popular form of cryptocurrency, where it serves as a public ledger for all network transactions. Bitcoin blockchain file sizes, which contained all transactions and records on the network, continued to grow substantially. By August 2014, it had reached 20 gigabytes, and eventually exceeded 200 gigabytes by early 2020.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain
Like all forms of technology, blockchain has several advantages and disadvantages to consider.
Advantages
One major advantage of blockchains is the level of security it can provide, and this also means that blockchains can protect and secure sensitive data from online transactions. For anyone looking for speedy and convenient transactions, blockchain technology offers this as well. In fact, it only takes a few minutes, whereas other transaction methods can take several days to complete. There is also no third-party interference from financial institutions or government organizations, which many users look at as an advantage.
Disadvantages
Blockchain and cryptography involves the use of public and private keys, and reportedly, there have been problems with private keys. If a user loses their private key, they face numerous challenges, making this one disadvantage of blockchains. Another disadvantage is the scalability restrictions, as the number of transactions per node is limited. Because of this, it can take several hours to finish multiple transactions and other tasks. It can also be difficult to change or add information after it is recorded, which is another significant disadvantage of blockchain.
|
Find Our Blockchain Training in Top Cities |
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
How is Blockchain Used?
Blockchains store information on monetary transactions using cryptocurrencies, but they also store other types of information, such as product tracking and other data. For example, food products can be tracked from the moment they are shipped out, all throughout their journey, and up until final delivery. This information can be helpful because if there is a contamination outbreak, the source of the outbreak can be easily traced. This is just one of the many ways that blockchains can store important data for organizations.
Hyperledger, Hosted by the Linux Foundation
Hyperledger is a global collaboration hosted by The Linux Foundation, including finance, banking, IoT, supply chain, manufacturing, and technology leaders. By creating a cross-industry open standard for distributed ledgers, Hyperledger Fabric allows developers to develop blockchain applications to meet specific needs.
Ten Steps to Your First Blockchain Application
- Understand what Blockchain is and its key components.
- Understand the purpose of your application.
- Create a use case for your application.
- Find out if there’s already an existing blockchain for your purpose.
- Explore the different types of Blockchain platforms available for your application. There are many types of Blockchain, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
- Choose the right platform for developing your app.
- Select the consensus algorithm you will use.
- Learn Solidity – Ethereum’s programming language for smart contracts and DApps (decentralized applications).
- Learn how to use Truffle or Remix – development tools for Ethereum DApps and smart contracts.
- Get an Ethereum account or wallet and buy some Ether (ETH), the currency of the Ethereum network.
Decentralization
Decentralization is difficult to Understand, but it is vital in the world today; decentralization is distributing or dispersing functions, powers, people, or things away from a central location or authority. Within the business world, decentralization typically refers to delegating authority from senior executives to middle managers and other employees further down the organizational hierarchy. The benefits of devolution are many and varied, but the most commonly cited advantages include improved communication, greater employee empowerment, and increased flexibility and responsiveness.
Transparency
One of the most critical aspects of decentralization is transparency. All employees have access to information and decision-making processes in a decentralized organization. This transparency fosters a greater sense of trust and cooperation among employees. Furthermore, it allows employees to hold managers accountable for their decisions.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
Bitcoin vs. Blockchain
Bitcoin is a digital currency that was first introduced in 2009 and has been the most popular and successful cryptocurrency to date. Bitcoin’s popularity is attributed to its decentralized nature, which means it doesn’t have a central authority or bank controlling its supply. This also means that transactions are anonymous, and no transaction fees are involved when using bitcoin.
Blockchain is a database of transactions that have taken place between two parties, with blocks of data containing information about each transaction being added in chronological order to the chain as it happens. The Blockchain is constantly growing as new blocks are added to it, with records becoming more difficult to change over time due to the number of blocks created after them.
Blockchain vs. Banks
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the banking industry. Banks need to be faster to adapt to the changing needs of the digital age, and Blockchain provides a way for them to catch up. By using Blockchain, banks can offer their customers a more secure and efficient way to conduct transactions. In addition, Blockchain can help banks to streamline their operations and reduce costs.
Why is Blockchain Important?
Blockchain is important because it has the potential to revolutionize the banking industry. Banks need to be faster to adapt to the changing needs of the digital age, and Blockchain provides a way for them to catch up. By using Blockchain, banks can offer their customers a more secure and efficient way to conduct transactions. In addition, Blockchain can help banks to streamline their operations and reduce costs.
What is a Blockchain Platform?
A blockchain platform is a shared digital ledger that allows users to record transactions and share information securely, tamper-resistant. A distributed network of computers maintains the register, and each transaction is verified by consensus among the network participants.
Proof of Work (PoW) vs. Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of work (PoW) is an algorithm to create blocks and secure the Blockchain. It requires miners to solve a puzzle to create a block and receive the block reward in return.
Proof of stake (PoS) is an alternative algorithm for securing the Blockchain, which does not require mining. Instead, users must lock up some of their coins for a certain time to be eligible for rewards.
Energy Consumption Concerns of Blockchain
The main concern with blockchain technology is its energy consumption. Traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, use a consensus mechanism called PoW( Proof of Work), which requires computational power and electricity to solve complex mathematical puzzles. This energy-intensive process has raised concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology because it produces carbon emissions and consumes a huge amount of electricity.
Blockchain or Scalability Trilemma: Decentralization, Security, and Scalability
Blockchain is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of records called blocks. Blockchain is often said to have the potential to disrupt many industries, including banking, law, and healthcare.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
What are the Benefits of Blockchains Over Traditional Finance?
Blockchain offers several potential advantages over traditional finance. One of the most touted advantages is that Blockchain is decentralized, while traditional finance is centralized. This means there is no single point of failure in a blockchain system. Another advantage of Blockchain is that it is more transparent than traditional finance.
Promising Blockchain Use Cases and Killer Applications
Promising Blockchain Use Cases and Killer Applications: Although there are many potential applications for blockchain technology, there are a few that stand out as having the potential to be truly game-changing. These are often referred to as killer applications. Some of the most promising killer applications for blockchain technology include supply chain management, identity management, and data management.
Promising blockchain use cases and killer applications are being developed every day. The Shiba Inu team is committed to finding and developing the most promising applications for the SHIB community. The team has a proven track record in the cryptocurrency space, and they are committed to creating value for the SHIB community.
How to Invest in Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology and stocks can be a lucrative investment, and there are several ways to take the next step toward making your first blockchain investment purchase. Bitcoin is typically the first thing that comes to mind when it comes to investing in blockchain technology, and it shouldn’t be overlooked. Aside from Bitcoin, there is also the option of investing in cryptocurrency penny stocks, such as Altcoin and Litecoin. There are also certain apps and services that are in the pre-development phase and that are using blockchain technology to raise funding. As an investor, you can buy coins, with the expectation that prices will go up if the service or app becomes popular. Another way to invest in blockchain technology is to invest in startups built on blockchain technology. Finally, there is always the option to invest in pure blockchain technology.
Traditional Finance and Blockchain Investment Strategies
In traditional finance, there are two main investment strategies: active and passive. Active investing involves picking stocks or other assets, and then holding onto them for a long period of time. Passive investing, on the other hand, involves investing in a basket of assets, and then holding onto them for a long period of time. Both of these strategies have their pros and cons, but there is one major difference between them: active investing is much more risky than passive investing.
How Do Different Industries Use Blockchain?
Blockchain has the potential to streamline processes across many different industries.
- In the supply chain industry, for example, Blockchain can track the movement of goods and materials as they change hands. This would allow for greater transparency and accountability and reduce the risk of fraud.
- In the healthcare industry, Blockchain can be used to secure patient data and streamline the process of billing and claims.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
What are the Features of Blockchain Technology?
- Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that is secure, transparent, and immutable.
- Blockchain technology can be used to create a decentralized database that is tamper-proof and has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with the digital world.
- Blockchain technology is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof.
What are the Key Components of Blockchain Technology?
There are three key components to blockchain technology:
- The distributed ledger, the consensus mechanism, and the smart contracts.
- The distributed ledger is a database that is spread across a network of computers. The consensus mechanism is what allows the network of computers to agree on the state of the ledger.
- The smart contracts are what allows the blockchain to be used for more than just a database.
What are Blockchain Protocols?
The three most common protocols Bitcoin was the first blockchain protocol and is still the most widely used is:
- Bitcoin- Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, often referred to as a cryptocurrency. It exists on a decentralized network of computers, often called a blockchain, that keeps track of all transactions made using the currency. Bitcoin uses a proof-of-work algorithm to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency to be created and is the most well-known.
- Ripple- Ripple is a cryptocurrency that is similar to Bitcoin. Ripple uses a decentralized network of computers to keep track of all transactions made using the currency. Ripple uses a proof-of-work algorithm to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Ripple was created in 2012 and is the second largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
- Ethereum- The Ethereum blockchain was initially described in a white paper by Vitalik Buterin in 2013. Buterin, a programmer who was born in Russia and raised in Canada, had been involved with bitcoin from its early days. He was excited by the technology, but he thought that bitcoin needed a scripting language for application development. He decided to create a new platform that would be more general than bitcoin.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
What is the Difference Between a Database and a Blockchain?
So what is the difference between a database and a blockchain? A database is centralized, meaning that a single entity controls it. This entity can be a company, government, or individual. On the other hand, a blockchain is decentralized, meaning that any entity does not control it.
How is Blockchain Different From the Cloud?
Blockchain is a new technology that is different from the cloud in several ways:
- Blockchain is decentralized, while the cloud is centralized. This means that Blockchain is distributed across a network of computers, while the cloud is stored on a central server.
- Blockchain is immutable, meaning that once data is written to the Blockchain, it cannot be changed.
What is Blockchain as a Service?
Blockchain as a Service is a cloud-based offering that allows customers to build, host, and use their blockchain applications, smart contracts, and functions on the Azure cloud platform. Azure offers integrated services that make it easy to develop, deploy, and manage blockchain applications. Customers can use Azure’s managed services to create and deploy blockchain applications without having to set up and manage their infrastructure.
Basics to Advanced – Learn It All!
Caltech PGP Full Stack DevelopmentExplore Program![]()
What are the Implications of Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology has made a great impact on society, including:
- Bitcoin, Blockchain’s prime application and the whole reason the technology was developed in the first place, has helped many people through financial services such as digital wallets. It has provided microloans and allowed micropayments to people in less than ideal economic circumstances, thereby introducing new life in the world economy.
- The next major impact is in the concept of TRUST, especially within the sphere of international transactions. Previously, lawyers were hired to bridge the trust gap between two different parties, but it consumed extra time and money. But the introduction of Cryptocurrency has radically changed the trust equation. Many organizations are located in areas where resources are scarce, and corruption is widespread. In such cases, Blockchain renders a significant advantage to these affected people and organizations, allowing them to escape the tricks of unreliable third-party intermediaries.
- The new reality of the Internet of Things (IoT) is already teeming with smart devices that — turn on your washing machines; drive your cars; navigate your ships; organize trash pick-up; manage traffic safety in your community — you name it! This is where blockchain comes in. In all of these cases (and more), leveraging blockchain technology by creating Smart Contracts will enable any organization to ‒ both — improve operations and keep more accurate records.
- Blockchain technology enables a decentralized peer-to-peer network for organizations or apps like Airbnb and Uber. It allows people to pay for things like toll fees, parking, etc.
- Blockchain technology can be used as a secure platform for the healthcare industry for the purposes of storing sensitive patient data. Health-related organizations can create a centralized database with the technology and share the information with only the appropriately authorized people.
- In the private consumer world, blockchain technology can be employed by two parties who wish to conduct a private transaction. However, these kinds of transactions have details that need to be hammered out before both parties can proceed:
- What are the terms and conditions (T&C) of the exchange?
- Are all the terms clear?
- When does the exchange start?
- When will it finish?
- When is it unfair to halt the exchange?
Since blockchain technology employs a shared ledger, distributed ledger on a decentralized network, all parties involved can quickly find answers to these questions by researching “blocks” in the “chain.” Transactions on a blockchain platform can be tracked from departure to the destination by all of the transactions on the chain.
How Can Features of Blockchain Support Sustainability Efforts
In spite of huge energy consumption the blockchain technology has features that can support sustainability efforts. For example:
Blockchain can give transparency and traceability in supply chains, allowing consumers to verify the origins and sustainability of products. This can encourage sustainable practices and discourage unethical practices such as deforestation, illegal fishing, or labor exploitation.
Decentralization: Blockchain’s decentralized nature helps to eliminate the need for intermediaries and reduce costs and also to increase efficiency. This can enable more direct and transparent transactions, reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional intermediaries.
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts that run on blockchain which eliminates the requirements for intermediaries and automating processes. This can reduce paperwork to minimize the disputes and streamline operations. It can help to lead to greater sustainability by reducing paper waste by increasing resource utilization.
Tokenization: Blockchain enables tokenization where assets can be represented as digital tokens. This can enable fractional ownership and make the process easier for people who intend to invest in sustainable assets such as renewable energy projects or carbon credits, promoting green investments and supporting sustainability initiatives.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a ground-breaking system that guarantees safe, open, and unchangeable transactions in a variety of sectors. It functions by utilizing cryptographic methods, decentralizing data storage, and producing immutable ledgers. There are several uses for this technology, including supply chain management and cryptocurrency. Comprehensive training is available for people who want to use blockchain in their jobs with Simplilearn’s Full Stack Java Developer certification. This curriculum gives you the fundamental knowledge of web development and blockchain technologies you need to create creative solutions in the rapidly changing IT industry.
In this blockchain program, you will learn how to master blockchain concepts, techniques, and tools like Truffle, Hyperledger, and Ethereum to build blockchain applications and networks.
FAQs
1. What is Blockchain in Simple Terms?
Blockchain is a shareable ledger that records transactions and is difficult to modify or change. It also tracks tangible and intangible assets such as cash or a house.
2. How Many Blockchains Are There?
There are 4 types of blockchain networks currently – public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains, and hybrid blockchains.
3. What’s the Difference Between a Private Blockchain and a Public Blockchain?
Private blockchains are only open to selected people, while public blockchain is open to the general masses. Private blockchains are more secure compared to public ones.
4. What is a Blockchain Platform?
A Blockchain Platform is any platform that exists to support or facilitate Blockchains. There are many types of blockchain platforms for different needs, such as Ethereum, Hyperledger, etc.
5. Who Invented Blockchain?
Blockchain was created by unknown persons under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto when they designed the online currency, Bitcoin.
6. What is Blockchain used for?
While most popularly used for digital currency such as Bitcoin, Blockchain is also now used in different sectors to safeguard records.
7. What are the 3 Pillars of Blockchain Technology?
Decentralization, Transparency, and Immutability are the 3 main pillars of blockchain technology.
8. Who Controls the Blockchain?
In blockchain, the power is divided between all of the users operating on the network. No single user has any control.
9. Why is Blockchain Important?
Blockchain offers security, transparency, and trust between the entire network of users. It also offers cost saving and efficient methods for data recording and sharing.
Tech
Harvard Alumni, Tech Moguls, and Best-Selling Authors Drive Nearly $600 Million in Pre-Order Sales

BlockDAG Network’s history is one of innovation, perseverance, and a vision to push the boundaries of blockchain technology. With Harvard alumni, tech moguls, and best-selling authors at the helm, BlockDAG is rewriting the rules of the cryptocurrency game.
CEO Antony Turner, inspired by the successes and shortcomings of Bitcoin and Ethereum, says, “BlockDAG leverages existing technology to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.” This powerhouse team has led a staggering 1,600% price increase in 20 pre-sale rounds, raising over $63.9 million. The secret? Unparalleled expertise and a bold vision for the future of blockchain.
Let’s dive into BlockDAG’s success story and find out what the future holds for this cryptocurrency.
The Origin: Why BlockDAG Was Created
In a recent interview, BlockDAG CEO Antony Turner perfectly summed up why the market needs BlockDAG’s ongoing revolution. He said:
“The creation of BlockDAG was inspired by Bitcoin and Ethereum, their successes and their shortcomings.
If you look at almost any new technology, it is very rare that the first movers remain at the forefront forever. Later incumbents have a huge advantage in entering a market where the need has been established and the technology is no longer cutting edge.
BlockDAG has done just that: our innovation is incorporating existing technology to provide a better solution, allowing us to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.”
The Present: How Far Has BlockDAG Come?
BlockDAG’s presale is setting new benchmarks in the cryptocurrency investment landscape. With a stunning 1600% price increase over 20 presale lots, it has already raised over $63.9 million in capital, having sold over 12.43 billion BDAG coins.
This impressive performance underscores the overwhelming confidence of investors in BlockDAG’s vision and leadership. The presale attracted over 20,000 individual investors, with the BlockDAG community growing exponentially by the hour.

These monumental milestones have been achieved thanks to the unparalleled skills, experience and expertise of BlockDAG’s management team:
Antony Turner – Chief Executive Officer
Antony Turner, CEO of BlockDAG, has over 20 years of experience in the Fintech, EdTech, Travel and Crypto industries. He has held senior roles at SPIRIT Blockchain Capital and co-founded Axona-Analytics and SwissOne. Antony excels in financial modeling, business management and scaling growth companies, with expertise in trading, software, IoT, blockchain and cryptocurrency.
Director of Communications
Youssef Khaoulaj, CSO of BlockDAG, is a Smart Contract Auditor, Metaverse Expert, and Red Team Hacker. He ensures system security and disaster preparedness, and advises senior management on security issues.
advisory Committee
Steven Clarke-Martin, a technologist and consultant, excels in enterprise technology, startups, and blockchain, with a focus on DAOs and smart contracts. Maurice Herlihy, a Harvard and MIT graduate, is an award-winning computer scientist at Brown University, with experience in distributed computing and consulting roles, most notably at Algorand.
The Future: Becoming the Cryptocurrency with the Highest Market Cap in the World
Given its impressive track record and a team of geniuses working tirelessly behind the scenes, BlockDAG is quickly approaching the $600 million pre-sale milestone. This crypto powerhouse will soon enter the top 30 cryptocurrencies by market cap.
Currently trading at $0.017 per coin, BlockDAG is expected to hit $1 million in the coming months, with the potential to hit $30 per coin by 2030. Early investors have already enjoyed a 1600% ROI by batch 21, fueling a huge amount of excitement around BlockDAG’s presale. The platform is seeing significant whale buying, and demand is so high that batch 21 is almost sold out. The upcoming batch is expected to drive prices even higher.

Invest in BlockDAG Pre-Sale Now:
Pre-sale: https://purchase.blockdag.network
Website: https://blockdag.network
Telegram: https://t.me/blockDAGnetwork
Discord: Italian: https://discord.gg/Q7BxghMVyu
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
How Karak’s Latest Tech Integration Could Make Data Breaches Obsolete

- Space and Time uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure secure and tamper-proof data processing for smart contracts and enterprises.
- The integration facilitates faster development and deployment of Distributed Secure Services (DSS) on the Karak platform.
Karak, a platform known for its strong security capabilities, is enhancing its Distributed Secure Services (DSS) by integrating Space and Time as a zero-knowledge (ZK) coprocessor. This move is intended to strengthen trustless operations across its network, especially in slashing and rewards mechanisms.
Space and Time is a verifiable processing layer that uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure that computations on decentralized data warehouses are secure and untampered with. This system enables smart contracts, large language models (LLMs), and enterprises to process data without integrity concerns.
The integration with Karak will enable the platform to use Proof of SQL, a new ZK-proof approach developed by Space and Time, to confirm that SQL query results are accurate and have not been tampered with.
One of the key features of this integration is the enhancement of DSS on Karak. DSS are decentralized services that use re-staked assets to secure the various operations they provide, from simple utilities to complex marketplaces. The addition of Space and Time technology enables faster development and deployment of these services, especially by simplifying slashing logic, which is critical to maintaining security and trust in decentralized networks.
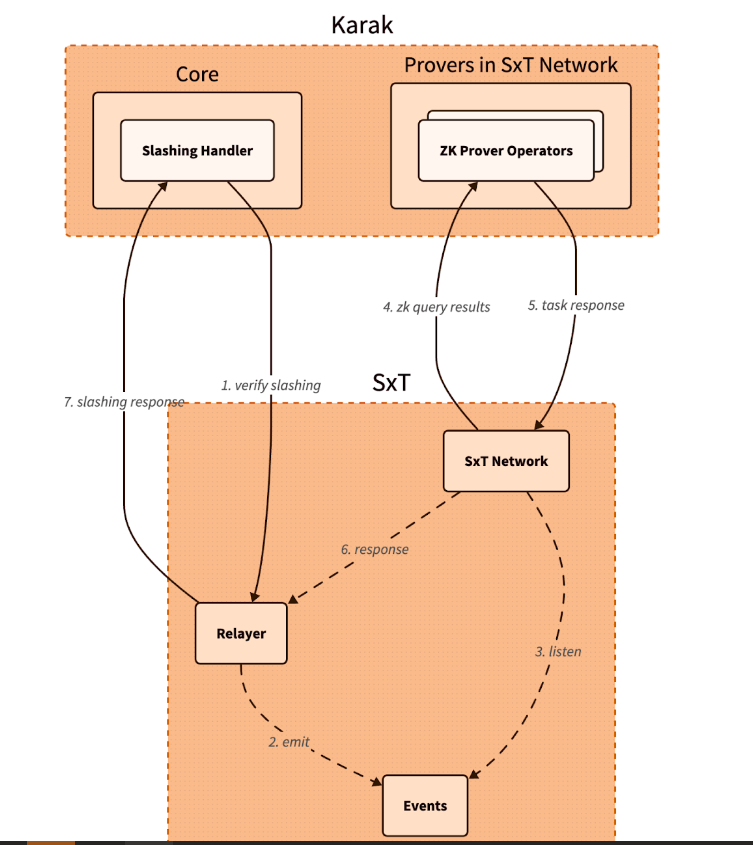
Additionally, Space and Time is developing its own DSS for blockchain data indexing. This service will allow community members to easily participate in the network by running indexing nodes. This is especially beneficial for applications that require high security and decentralization, such as decentralized data indexing.
The integration architecture follows a detailed and secure flow. When a Karak slashing contract needs to verify a SQL query, it calls the Space and Time relayer contract with the required SQL statement. This contract then emits an event with the query details, which is detected by operators in the Space and Time network.
These operators, responsible for indexing and monitoring DSS activities, validate the event and route the work to a verification operator who runs the query and generates the necessary ZK proof.
The result, along with a cryptographic commitment on the queried data, is sent to the relayer contract, which verifies and returns the data to the Karak cutter contract. This end-to-end process ensures that the data used in decision-making, such as determining penalties within the DSS, is accurate and reliable.
Karak’s mission is to provide universal security, but it also extends the capabilities of Space and Time to support multiple DSSs with their data indexing needs. As these technologies evolve, they are set to redefine the secure, decentralized computing landscape, making it more accessible and efficient for developers and enterprises alike. This integration represents a significant step towards a more secure and verifiable digital infrastructure in the blockchain space.
Website | X (Twitter) | Discord | Telegram
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
Cryptocurrency Payments: Should CFOs Consider This Ferrari-Approved Trend?

Iconic Italian luxury carmaker Ferrari has announced the expansion of its cryptocurrency payment system to its European dealer network.
The move, which follows a successful launch in North America less than a year ago, raises a crucial question for CFOs across industries: Is it time to consider accepting cryptocurrency as a form of payment for your business?
Ferrari’s move isn’t an isolated one. It’s part of a broader trend of companies embracing digital assets. As of 2024, we’re seeing a growing number of companies, from tech giants to traditional retailers, accepting cryptocurrencies.
This change is determined by several factors:
- Growing mainstream adoption of cryptocurrencies
- Growing demand from tech-savvy and affluent consumers
- Potential for faster and cheaper international transactions
- Desire to project an innovative brand image
Ferrari’s approach is particularly noteworthy. They have partnered with BitPay, a leading cryptocurrency payment processor, to allow customers to purchase vehicles using Bitcoin, Ethereum, and USDC. This satisfies their tech-savvy and affluent customer base, many of whom have large digital asset holdings.
Navigating Opportunities and Challenges
Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments illustrates several key opportunities for companies considering this move. First, it opens the door to new customer segments. By accepting cryptocurrency, Ferrari is targeting a younger, tech-savvy demographic—people who have embraced digital assets and see them as a legitimate form of value exchange. This strategy allows the company to connect with a new generation of affluent customers who may prefer to conduct high-value transactions in cryptocurrency.
Second, cryptocurrency adoption increases global reach. International payments, which can be complex and time-consuming with traditional methods, become significantly easier with cryptocurrency transactions. This can be especially beneficial for businesses that operate in multiple countries or deal with international customers, as it potentially reduces friction in cross-border transactions.
Third, accepting cryptocurrency positions a company as innovative and forward-thinking. In today’s fast-paced business environment, being seen as an early adopter of emerging technologies can significantly boost a brand’s image. Ferrari’s move sends a clear message that they are at the forefront of financial innovation, which can appeal to customers who value cutting-edge approaches.
Finally, there is the potential for cost savings. Traditional payment methods, especially for international transactions, often incur substantial fees. Cryptocurrency transactions, on the other hand, can offer lower transaction costs. For high-value purchases, such as luxury cars, these savings could be significant for both the business and the customer.
While the opportunities are enticing, accepting cryptocurrency payments also presents significant challenges that businesses must address. The most notable of these is volatility. Cryptocurrency values can fluctuate dramatically, sometimes within hours, posing potential risk to businesses that accept them as payment. Ferrari addressed this challenge by implementing a system that instantly converts cryptocurrency received into traditional fiat currencies, effectively mitigating the risk of value fluctuations.
Regulatory uncertainty is another major concern. The legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies is still evolving in many jurisdictions around the world. This lack of clear and consistent regulations can create compliance challenges for companies, especially those operating internationally. Companies must remain vigilant and adaptable as new laws and regulations emerge, which can be a resource-intensive process.
Implementation costs are also a significant obstacle. Integrating cryptocurrency payment systems often requires substantial investment in new technology infrastructure and extensive staff training. This can be especially challenging for small businesses or those with limited IT resources. The costs are not just financial; a significant investment of time is also required to ensure smooth implementation and operation.
Finally, security concerns loom large in the world of cryptocurrency transactions. While blockchain technology offers some security benefits, cryptocurrency transactions still require robust cybersecurity measures to protect against fraud, hacks, and other malicious activity. Businesses must invest in robust security protocols and stay up-to-date on the latest threats and protections, adding another layer of complexity and potential costs to accepting cryptocurrency payments.
Strategic Considerations for CFOs
If you’re thinking of following in Ferrari’s footsteps, here are the key factors to consider:
- Risk Assessment: Carefully evaluate potential risks to your business, including financial, regulatory, and reputational risks.
- Market Analysis: Evaluate whether your customer base is significantly interested in using cryptocurrencies for payments.
- Technology Infrastructure: Determine the costs and complexities of implementing a cryptographic payment system that integrates with existing financial processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that cryptocurrency acceptance is in line with local regulations in all markets you operate in. Ferrari’s gradual rollout demonstrates the importance of this consideration.
- Financial Impact: Analyze how accepting cryptocurrency could impact your cash flow, accounting practices, and financial reporting.
- Partnership Evaluation: Consider partnering with established crypto payment processors to reduce risk and simplify implementation.
- Employee Training: Plan comprehensive training to ensure your team is equipped to handle cryptocurrency transactions and answer customer questions.
While Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments is exciting, it’s important to consider this trend carefully.
A CFO’s decision to adopt cryptocurrency as a means of payment should be based on a thorough analysis of your company’s specific needs, risk tolerance, and strategic goals. Cryptocurrency payments may not be right for every business, but for some, they could provide a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Remember that the landscape is rapidly evolving. Stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. Whether you decide to accelerate your crypto engines now or wait in the pit, keeping this payment option on your radar is critical to navigating the future of business transactions.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
Sign up to receive your daily business insights
Tech
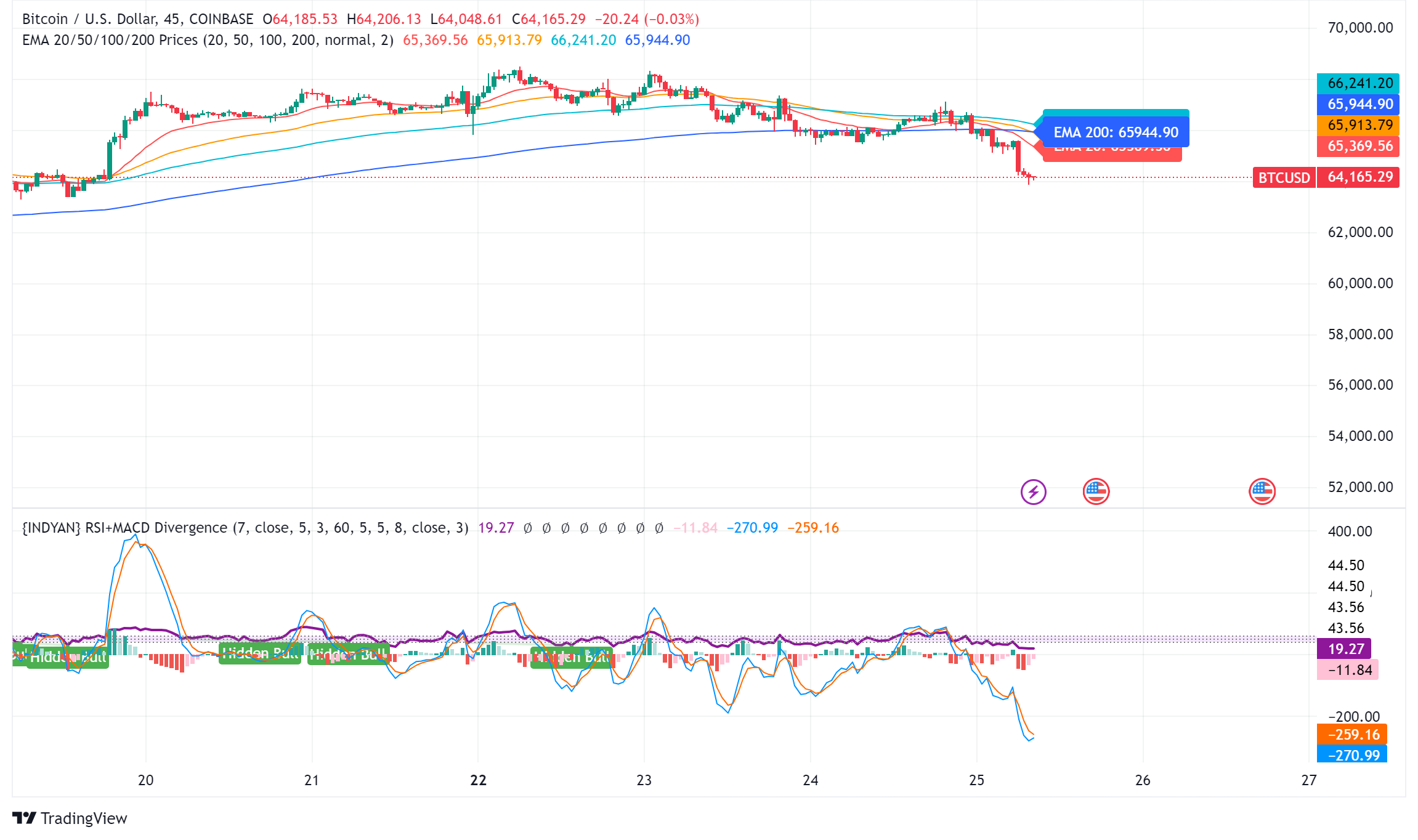
Bitcoin Tumbles as Crypto Market Selloff Mirrors Tech Stocks’ Plunge
The world’s largest cryptocurrency, Bitcoin (BTC), suffered a significant price decline on Wednesday, falling below $65,000. The decline coincides with a broader market sell-off that has hit technology stocks hard.
Cryptocurrency Liquidations Hit Hard
CoinGlass data reveals a surge in long liquidations in the cryptocurrency market over the past 24 hours. These liquidations, totaling $220.7 million, represent forced selling of positions that had bet on price increases. Bitcoin itself accounted for $14.8 million in long liquidations.
Ethereum leads the decline
Ethereal (ETH), the second-largest cryptocurrency, has seen a steeper decline than Bitcoin, falling nearly 8% to trade around $3,177. This decline mirrors Bitcoin’s price action, suggesting a broader market correction.
Cryptocurrency market crash mirrors tech sector crash
The cryptocurrency market decline appears to be linked to the significant losses seen in the U.S. stock market on Wednesday. Stock market listing The index, heavily weighted toward technology stocks, posted its sharpest decline since October 2022, falling 3.65%.
Analysts cite multiple factors
Several factors may have contributed to the cryptocurrency market crash:
- Tech earnings are underwhelming: Earnings reports from tech giants like Alphabet are disappointing (Google(the parent company of), on Tuesday, triggered a sell-off in technology stocks with higher-than-expected capital expenditures that could have repercussions on the cryptocurrency market.
- Changing Political Landscape: The potential impact of the upcoming US elections and changes in Washington’s policy stance towards cryptocurrencies could influence investor sentiment.
- Ethereal ETF Hopes on the line: While bullish sentiment around a potential U.S. Ethereum ETF initially boosted the market, delays or rejections could dampen enthusiasm.
Analysts’ opinions differ
Despite the short-term losses, some analysts remain optimistic about Bitcoin’s long-term prospects. Singapore-based cryptocurrency trading firm QCP Capital believes Bitcoin could follow a similar trajectory to its post-ETF launch all-time high, with Ethereum potentially converging with its previous highs on sustained institutional interest.
Rich Dad Poor Dad Author’s Prediction
Robert Kiyosaki, author of the best-selling Rich Dad Poor Dad, predicts a potential surge in the price of Bitcoin if Donald Trump is re-elected as US president. He predicts a surge to $105,000 per coin by August 2025, fueled by a weaker dollar that is set to boost US exports.
BTC/USD Technical Outlook
Bitcoin price is currently trading below key support levels, including the $65,500 level and the 100 hourly moving average. A break below the $64,000 level could lead to further declines towards the $63,200 support zone. However, a recovery above the $65,500 level could trigger another increase in the coming sessions.
-

 Videos1 month ago
Videos1 month agoAbsolutely massive: the next higher Bitcoin leg will shatter all expectations – Tom Lee
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoVolta Finance Limited – Director/PDMR Shareholding
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoModiv Industrial to release Q2 2024 financial results on August 6
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoApple to report third-quarter earnings as Wall Street eyes China sales
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoNumber of Americans filing for unemployment benefits hits highest level in a year
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoInventiva reports 2024 First Quarter Financial Information¹ and provides a corporate update
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoLeeds hospitals trust says finances are “critical” amid £110m deficit
-

 Markets1 year ago
Markets1 year agoWhale Investments in Bitcoin Hit $100 Billion in 2024, Fueling Insane Investor Optimism ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 DeFi1 year ago
DeFi1 year ago🏴☠️ Pump.Fun operated by Insider Exploit
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year ago$1,000,000 worth of BTC in 2025! Get ready for an UNPRECEDENTED PRICE EXPLOSION – Jack Mallers
-
 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoABSOLUTELY HUGE: Bitcoin is poised for unabated exponential growth – Mark Yusko and Willy Woo
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoBlockDAG ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Review: Is It the Next Big Thing in Cryptocurrency? 5 questions answered





