Tech
Blockchain technology for mobile multi-robot systems
Dudek, G., Jenkin, M. R., Milios, E. & Wilkes, D. A taxonomy for multi-agent robotics. Autonomous Robot. 3, 375–397 (1996).
Parker, L. E. Multiple mobile robot systems. In Springer Handbook of Robotics 921–941 (Springer, 2008). This paper presents an accessible introduction to the foundations and early successes of mobile multi-robot systems.
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z., Siegwart, R. & Chung, J. J. Distributed PDOP coverage control: providing large-scale positioning service using a multi-robot system. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6, 2217–2224 (2021).
Mathews, N., Christensen, A. L., O’Grady, R., Mondada, F. & Dorigo, M. Mergeable nervous systems for robots. Nat. Commun. 8, 439 (2017).
Timmis, J., Ismail, A. R., Bjerknes, J. D. & Winfield, A. F. T. An immune-inspired swarm aggregation algorithm for self-healing swarm robotic systems. Biosystems 146, 60–76 (2016).
Mathews, N., Christensen, A. L., Stranieri, A., Scheidler, A. & Dorigo, M. Supervised morphogenesis: exploiting morphological flexibility of self-assembling multirobot systems through cooperation with aerial robots. Robot. Autonomous Syst. 112, 154–167 (2019).
Rizk, Y., Awad, M. & Tunstel, E. W. Cooperative heterogeneous multi-robot systems: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 52, https://doi.org/10.1145/3303848 (2019). This paper presents an overview of recent research achievements as well as open challenges in multi-robot systems.
Dorigo, M., Theraulaz, G. & Trianni, V. Swarm robotics: past, present and future. Proc. IEEE 109, 1152–1165 (2021). This review surveys the past, present and future of swarm robotics, discussing open challenges and research directions.
Wurman, P., D’Andrea, R. & Mountz, M. Coordinating hundreds of cooperative, autonomous vehicles in warehouses. AI Mag. 29, 9–20 (2008).
Yang, G.-Z. et al. The grand challenges of Science Robotics. Sci. Robot. 3, eaar7650 (2018).
Dorigo, M., Theraulaz, G. & Trianni, V. Reflections on the future of swarm robotics. Sci. Robot. 5, abe4385 (2020).
Wilson, J. et al. Trustworthy swarms. In Proc. First Int. Symp. Trustworthy Autonomous Systems https://doi.org/10.1145/3597512.3599705 (ACM, 2023).
Strobel, V., Castelló Ferrer, E. & Dorigo, M. Managing Byzantine robots via blockchain technology in a swarm robotics collective decision making scenario. In Proc. 17th Int. Conf. Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2018) 541–549 (IFAAMAS, 2018).
Castelló Ferrer, E., Hardjono, T., Pentland, A. & Dorigo, M. Secure and secret cooperation in robot swarms. Sci. Robot. 6, abf1538 (2021).
Hunt, E. R. & Hauert, S. A checklist for safe robot swarms. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2, 420–422 (2020). This paper presents a ten-item checklist to determine whether a robot swarm is safe.
Castelló Ferrer, E. If blockchain is the solution, robot security is the problem. Front. Blockchain 6, 1181820 (2023).
Strobel, V., Pacheco, A. & Dorigo, M. Robot swarms neutralize harmful Byzantine robots using a blockchain-based token economy. Sci. Robot. 8, eabm4636 (2023). This paper presents the first large-scale proof of concept of how to integrate blockchain technology into decentralized multi-robot systems.
Santos De Campos, M. G., Chanel, C. P., Chauffaut, C. & Lacan, J. Towards a blockchain-based multi-UAV surveillance system. Front. Robot. AI 8, 557692 (2021).
Grey, J., Godage, I. & Seneviratne, O. Swarm contracts: Smart contracts in robotic swarms with varying agent behavior. In Proc. 2020 IEEE Int. Conf. Blockchain (Blockchain 2020) 265–272 (IEEE, 2020).
Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. https://bitcoin.org/en/bitcoin-paper (2008). This article describes the first practical implementation of a consensus-based decentralized digital currency that overcomes the Byzantine generals problem and introduces blockchain technology as a ledger for storing transactions of the cryptocurrency Bitcoin.
Buterin, V. A next-generation smart contract and decentralized application platform. Ethereum Project white paper. Ethereum https://ethereum.org/en/whitepaper/ (2014). In this work the blockchain framework Ethereum generalizes the idea behind a blockchain from a store of value to a decentralized computing system, enabling smart contracts.
Peña Queralta, J. et al. Blockchain and emerging distributed ledger technologies for decentralized multi-robot systems. Curr. Robot. Rep. 4, 43–54 (2023).
Aditya, S., Singh, R., Singh, P. K. & Kalla, A. A survey on blockchain in robotics: issues, opportunities, challenges and future directions. J. Netw. Computer Appl. 196, 103245 (2021).
Peña Queralta, J. & Westerlund, T. Blockchain for mobile edge computing: Consensus mechanisms and scalability. In Mobile Edge Computing 333–357 (Springer, 2021).
Singh, A. et al. Sidechain technologies in blockchain networks: an examination and state-of-the-art review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 149, 102471 (2020).
Strobel, V. & Dorigo, M. Blockchain technology for robot swarms: A shared knowledge and reputation management system for collective estimation. In Swarm Intelligence—Proc. ANTS 2018—11th Int. Conf. 425–426 (Springer, 2018). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 11172].
Strobel, V., Castelló Ferrer, E. & Dorigo, M. Blockchain technology secures robot swarms: a comparison of consensus protocols and their resilience to Byzantine robots. Front. Robot. AI 7, 54 (2020).
Pacheco, A., Strobel, V. & Dorigo, M. A blockchain-controlled physical robot swarm communicating via an ad-hoc network. In Swarm Intelligence—Proc. ANTS 2020—12th Int. Conf. 3–15 (Springer, 2020). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 12421].
Pacheco, A., Strobel, V., Reina, A. & Dorigo, M. Real-time coordination of a foraging robot swarm using blockchain smart contracts. In Swarm Intelligence—Proc. ANTS 2022—13th Int. Conf. 196–208 (Springer, 2022). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 13491].
Castelló Ferrer, E., Jiménez, E., Lopez-Presa, J. L. & Martín-Rueda, J. Following leaders in Byzantine multirobot systems by using blockchain technology. IEEE Trans. Robot. 38, 1101–1117 (2021).
Alsamhi, S. H. et al. Blockchain-empowered security and energy efficiency of drone swarm consensus for environment exploration. IEEE Trans. Green. Commun. Netw. 7, 328–338 (2023).
Mokhtar, A., Murphy, N. & Bruton, J. Blockchain-based multi-robot path planning. In Proc. 5th IEEE World Forum on Internet of Things (WF–IoT 2019) 584–589 (IEEE, 2019).
Grey, J., Seneviratne, O. & Godage, I. Blockchain-based mechanism for robotic cooperation through incentives: Prototype application in warehouse automation. In Proc. 2021 IEEE Int. Conf. Blockchain (Blockchain 2021) 597–604 (IEEE, 2021).
Mallikarachchi, S., Dai, C., Seneviratne, O. & Godage, I. Managing collaborative tasks within heterogeneous robotic swarms using swarm contracts. In Proc. 4th IEEE Int. Conf. Decentralized Applications and Infrastructures (DAPPS 2022) 48–55 (IEEE, 2022).
Castelló Ferrer, E., Rudovic, O., Hardjono, T. & Pentland, A. Robochain: A secure data-sharing framework for human-robot interaction. In Proc. 10th Int. Conf. Health, Telemedicine, and Social Medicine (eTELEMED 2018) 124–130 (IARIA, 2018).
Alsamhi, S. H. & Lee, B. Blockchain-empowered multi-robot collaboration to fight COVID-19 and future pandemics. IEEE Access. 9, 44173–44197 (2021).
Kapitonov, A., Lonshakov, S., Bulatov, V., Montazam, B. K. & White, J. Robot-as-a-service: from cloud to peering technologies. Front. Robot. AI 8, 560829 (2021).
Kapitonov, A., Lonshakov, S., Krupenkin, A. & Berman, I. Blockchain-based protocol of autonomous business activity for multi-agent systems consisting of UAVs. In 2017 Workshop on Research, Education and Development of Unmanned Aerial Systems (RED-UAS) 84–89 (IEEE, 2017).
Ongaro, D. & Ousterhout, J. In search of an understandable consensus algorithm. In 2014 USENIX Annu. Technical Conf. (USENIX ATC 14) 305–319 (2014).
Androulaki, E. et al. Hyperledger Fabric: A distributed operating system for permissioned blockchains. In Proc. 13th EuroSys Conf. 1–15 (ACM, 2018).
Salimi, S., Peña Queralta, J. & Westerlund, T. Hyperledger Fabric blockchain and ROS 2 integration for autonomous mobile robots. In 2023 IEEE/SICE Int. Symp. System Integration 1–8 (IEEE, 2023).
Wardega, K., von Hippel, M., Tron, R., Nita-Rotaru, C. & Li, W. Byzantine resilience at swarm scale: A Decentralized Blocklist Protocol from inter-robot accusations. In Proc. 2023 Int. Conf. Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS ’23) 1430–1438 (IFAAMAS, 2023).
Hoffmann, F. Challenges of proof-of-useful-work (PoUW). In Proc. IEEE 1st Global Emerging Technology Blockchain Forum: Blockchain & Beyond (iGETblockchain 2022) https://doi.org/10.1109/iGETblockchain56591.2022.10087185 (IEEE, 2022).
Tran, J. A. et al. SwarmDAG: a partition tolerant distributed ledger protocol for swarm robotics. Ledger 4, https://doi.org/10.5195/ledger.2019.174 (2019).
Keramat, F., Peña Queralta, J. & Westerlund, T. Partition-tolerant and Byzantine-tolerant decision making for distributed robotic systems with IOTA and ROS2. IEEE Internet Things J. 10, 12985–12998 (2023).
Salimpour, S., Keramat, F., Peña Queralta, J. & Westerlund, T. Decentralized vision-based Byzantine agent detection in multi-robot systems with IOTA smart contracts. In Foundations and Practice of Security: 15th Int. Symp., FPS 2022, Revised Selected Papers 322–337 (Springer, 2023).
Al-Breiki, H., Rehman, M. H. U., Salah, K. & Svetinovic, D. Trustworthy blockchain oracles: review, comparison, and open research challenges. IEEE Access. 8, 85675–85685 (2020).
Mühlberger, R. et al. Foundational oracle patterns: Connecting blockchain to the off-chain world. In Business Process Management: Blockchain and Robotic Process Automation Forum 35–51 (Springer, 2020).
Zhao, H. et al. A generic framework for Byzantine-tolerant consensus achievement in robot swarms. In IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intelligent Robots and Systems—IROS 2023 8839–8846 (IEEE, 2023).
Valentini, G., Brambilla, D., Hamann, H. & Dorigo, M. Collective perception of environmental features in a robot swarm. In Swarm Intelligence—Proc. ANTS 2016—10th Int. Conf. 65–76 (Springer, 2016). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 9882].
Brekke, J. K. & Alsindi, W. Z. Cryptoeconomics. Internet Policy Rev. 10, https://doi.org/10.14763/2021.2.1553 (2021).
Andola, N., Raghav, Yadav, V. K., Venkatesan, S. & Verma, S. Anonymity on blockchain based e-cash protocols—a survey. Computer Sci. Rev. 40, 100394 (2021).
Conoscenti, M., Vetrò, A. & De Martin, J. C. Blockchain for the Internet of Things: A systematic literature review. In Proc. 13th IEEE/ACS Int. Conf. Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA 2016) 1–6 (2016).
Raymond, E. S. The Cathedral and the Bazaar: Musings on Linux and Open Source by an Accidental Revolutionary (O’Reilly Media, 1999).
Rodler, M., Li, W., Karame, G. O. & Davi, L. EVMPatch: Timely and automated patching of Ethereum smart contracts. In Proc. 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 21) 1289–1306 (USENIX Association, 2021).
DuPont, Q. Experiments in algorithmic governance: A history and ethnography of ‘The DAO,’ a failed decentralized autonomous organization. In Bitcoin and Beyond: Cryptocurrencies, Blockchains, and Global Governance 157–177 (Routledge, 2017).
Sabt, M., Achemlal, M., & Bouabdallah, A. Trusted Execution Environment: What it is, and what it is not. In Proc. 14th IEEE Int. Conf. Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications 57–64 (IEEE Press, 2015).
Wöhrer, M. & Zdun, U. Design patterns for smart contracts in the Ethereum ecosystem. In Proc. IEEE 2018 Int. Congress on Cybermatics 1513–1520 (IEEE, 2018).
Van Calck, L., Pacheco, A., Strobel, V., Dorigo, M. & Reina, A. A blockchain-based information market to incentivise cooperation in swarms of self-interested robots. Sci. Rep. 13, 20417 (2023).
Hassan, S. & De Filippi, P. Decentralized autonomous organization. Internet Policy Rev. 10, https://doi.org/10.14763/2021.2.1556 (2021).
Wang, S. et al. Decentralized autonomous organizations: concept, model, and applications. IEEE Trans. Computational Soc. Syst. 6, 870–878 (2019).
Cardenas, I. S., May, J. B. & Kim, J.-H. AutomataDAO: A blockchain-based data marketplace for interactive robot and IoT data exchanges using Ethermint and state channels. In Blockchain Technology for IoT Applications 17–38 (Springer, 2021).
Reina, A. Robot teams stay safe with blockchains. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2, 240–241 (2020).
Danilov, K., Rezin, R., Afanasyev, I. & Kolotov, A. Towards blockchain-based Robonomics: Autonomous agents behavior validation. In Proc 9th IEEE Int Conf Intelligent Systems (IS 2018) 222–227 (IEEE, 2018).
Abou Jaoude, J. & Saade, R. G. Blockchain applications—usage in different domains. IEEE Access. 7, 45360–45381 (2019).
Castelló Ferrer, E. et al. Gaka-chu: A self-employed autonomous robot artist. In Proc. 2023 IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2023) 11583–11589 (IEEE, 2023).
Lajoie, P.-Y., Ramtoula, B., Wu, F. & Beltrame, G. Towards collaborative simultaneous localization and mapping: a survey of the current research landscape. Field Robotics 2, 971–1000 (2022).
Chong, C.-Y., Chang, K.-C. & Mori, S. A review of forty years of distributed estimation. In Proc. 21st Int. Conf. Information Fusion (Fusion 2018) 1–8 (IEEE, 2018).
Douceur, J. R. The Sybil attack. In 1st International Workshop on Peer-to-Peer Systems 251–260 (Springer, 2002). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2429].
Saeedi, S., Trentini, M., Seto, M. & Li, H. Multiple‐robot simultaneous localization and mapping: a review. J. Field Robot. 33, 3–46 (2016).
Kegeleirs, M., Grisetti, G. & Birattari, M. Swarm SLAM: challenges and perspectives. Front. Robot. AI 8, 618268 (2021).
Majcherczyk, N., Srishankar, N. & Pinciroli, C. Flow-FL: Data-driven federated learning for spatio-temporal predictions in multi-robot systems. In Proc. 2021 IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2021) 8836–8842 (IEEE, 2021).
Zakir, R., Dorigo, M. & Reina, A. Robot swarms break decision deadlocks in collective perception through cross-inhibition. In Swarm Intelligence—Proc. ANTS 2022—3th Int. Conf. 209–221 (Springer, 2022). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 13491].
Castelló Ferrer, E. The blockchain: A new framework for robotic swarm systems. In Proc. Future Technol. Conf. (FTC 2018) Vol. 881 1037–1058 (Springer, 2018).
Maskin, E. Introduction to mechanism design and implementation. Transnatl. Corporations Rev. 11, 1–6 (2019).
White, R., Caiazza, G., Cortesi, A., Cho, Y. & Christensen, H. Black block recorder: immutable black box logging for robots via blockchain. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 4, 3812–3819 (2019).
Lopes, V. & Alexandre, L. A. Detecting robotic anomalies using Robotchain. In IEEE Int. Conf. Autonomous Robot Systems and Competitions (ICARSC 2019) 174–179 (IEEE, 2019).
Lopes, V., Pereira, N., Fernandes, M. & Alexandre, L. A. A time-segmented consortium blockchain for robotic event registration. In Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Blockchain Technology (ICBCT 2021) 117–122 (ACM, 2021).
Talamali, M. S., Saha, A., Marshall, J. A. R. & Reina, A. When less is more: robot swarms adapt better to changes with constrained communication. Sci. Robot. 6, eabf1416 (2021).
Zhu W. et al. Self-organizing nervous systems for robot swarms. Preprint at arXiv https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2401.13103 (2024).
Dorigo, M., Birattari, M. & Brambilla, M. Swarm robotics. Scholarpedia 9, 1463 (2014).
Hamann, H. Swarm Robotics: A Formal Approach (Springer, 2018).
Gielis, J., Shankar, A. & Prorok, A. A critical review of communications in multi-robot systems. Curr. Robot. Rep. 3, 213–225 (2022).
Demir, K. A., Döven, G. & Sezen, B. Industry 5.0 and human-robot co-working. Procedia Comput. Sci. 158, 688–695 (2019).
Lamport, L., Shostak, R. & Pease, M. The Byzantine generals problem. ACM Trans. Program. Lang. Syst. 4, 382–401 (1982). This foundational paper introduces the Byzantine generals problem — a thought experiment that highlights the challenges of achieving a consensus in distributed networks where the agents (the ‘Byzantine generals’) are not necessarily reliable.
Castro, M. & Liskov, B. Practical Byzantine fault tolerance and proactive recovery. ACM Trans. Computer Syst. 20, 398–461 (2002).
Dwork, C., Lynch, N. & Stockmeyer, L. Consensus in the presence of partial synchrony. J. ACM 35, 288–323 (1988).
Chaum, D., Fiat, A. & Naor, M. Untraceable electronic cash. In Advances in Cryptology—Crypto ’88 (Springer, 1990). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 403].
Dwork, C. & Naor, M. Pricing via processing or combatting junk mail. In Proc. Annu. Int. Cryptology Conf.—Advances in Cryptology (Crypto’ 92) 139–147 (Springer, 1992). [Lecture Notes in Computer Science 740].
Tech
Harvard Alumni, Tech Moguls, and Best-Selling Authors Drive Nearly $600 Million in Pre-Order Sales

BlockDAG Network’s history is one of innovation, perseverance, and a vision to push the boundaries of blockchain technology. With Harvard alumni, tech moguls, and best-selling authors at the helm, BlockDAG is rewriting the rules of the cryptocurrency game.
CEO Antony Turner, inspired by the successes and shortcomings of Bitcoin and Ethereum, says, “BlockDAG leverages existing technology to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.” This powerhouse team has led a staggering 1,600% price increase in 20 pre-sale rounds, raising over $63.9 million. The secret? Unparalleled expertise and a bold vision for the future of blockchain.
Let’s dive into BlockDAG’s success story and find out what the future holds for this cryptocurrency.
The Origin: Why BlockDAG Was Created
In a recent interview, BlockDAG CEO Antony Turner perfectly summed up why the market needs BlockDAG’s ongoing revolution. He said:
“The creation of BlockDAG was inspired by Bitcoin and Ethereum, their successes and their shortcomings.
If you look at almost any new technology, it is very rare that the first movers remain at the forefront forever. Later incumbents have a huge advantage in entering a market where the need has been established and the technology is no longer cutting edge.
BlockDAG has done just that: our innovation is incorporating existing technology to provide a better solution, allowing us to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.”
The Present: How Far Has BlockDAG Come?
BlockDAG’s presale is setting new benchmarks in the cryptocurrency investment landscape. With a stunning 1600% price increase over 20 presale lots, it has already raised over $63.9 million in capital, having sold over 12.43 billion BDAG coins.
This impressive performance underscores the overwhelming confidence of investors in BlockDAG’s vision and leadership. The presale attracted over 20,000 individual investors, with the BlockDAG community growing exponentially by the hour.

These monumental milestones have been achieved thanks to the unparalleled skills, experience and expertise of BlockDAG’s management team:
Antony Turner – Chief Executive Officer
Antony Turner, CEO of BlockDAG, has over 20 years of experience in the Fintech, EdTech, Travel and Crypto industries. He has held senior roles at SPIRIT Blockchain Capital and co-founded Axona-Analytics and SwissOne. Antony excels in financial modeling, business management and scaling growth companies, with expertise in trading, software, IoT, blockchain and cryptocurrency.
Director of Communications
Youssef Khaoulaj, CSO of BlockDAG, is a Smart Contract Auditor, Metaverse Expert, and Red Team Hacker. He ensures system security and disaster preparedness, and advises senior management on security issues.
advisory Committee
Steven Clarke-Martin, a technologist and consultant, excels in enterprise technology, startups, and blockchain, with a focus on DAOs and smart contracts. Maurice Herlihy, a Harvard and MIT graduate, is an award-winning computer scientist at Brown University, with experience in distributed computing and consulting roles, most notably at Algorand.
The Future: Becoming the Cryptocurrency with the Highest Market Cap in the World
Given its impressive track record and a team of geniuses working tirelessly behind the scenes, BlockDAG is quickly approaching the $600 million pre-sale milestone. This crypto powerhouse will soon enter the top 30 cryptocurrencies by market cap.
Currently trading at $0.017 per coin, BlockDAG is expected to hit $1 million in the coming months, with the potential to hit $30 per coin by 2030. Early investors have already enjoyed a 1600% ROI by batch 21, fueling a huge amount of excitement around BlockDAG’s presale. The platform is seeing significant whale buying, and demand is so high that batch 21 is almost sold out. The upcoming batch is expected to drive prices even higher.

Invest in BlockDAG Pre-Sale Now:
Pre-sale: https://purchase.blockdag.network
Website: https://blockdag.network
Telegram: https://t.me/blockDAGnetwork
Discord: Italian: https://discord.gg/Q7BxghMVyu
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
How Karak’s Latest Tech Integration Could Make Data Breaches Obsolete

- Space and Time uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure secure and tamper-proof data processing for smart contracts and enterprises.
- The integration facilitates faster development and deployment of Distributed Secure Services (DSS) on the Karak platform.
Karak, a platform known for its strong security capabilities, is enhancing its Distributed Secure Services (DSS) by integrating Space and Time as a zero-knowledge (ZK) coprocessor. This move is intended to strengthen trustless operations across its network, especially in slashing and rewards mechanisms.
Space and Time is a verifiable processing layer that uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure that computations on decentralized data warehouses are secure and untampered with. This system enables smart contracts, large language models (LLMs), and enterprises to process data without integrity concerns.
The integration with Karak will enable the platform to use Proof of SQL, a new ZK-proof approach developed by Space and Time, to confirm that SQL query results are accurate and have not been tampered with.
One of the key features of this integration is the enhancement of DSS on Karak. DSS are decentralized services that use re-staked assets to secure the various operations they provide, from simple utilities to complex marketplaces. The addition of Space and Time technology enables faster development and deployment of these services, especially by simplifying slashing logic, which is critical to maintaining security and trust in decentralized networks.
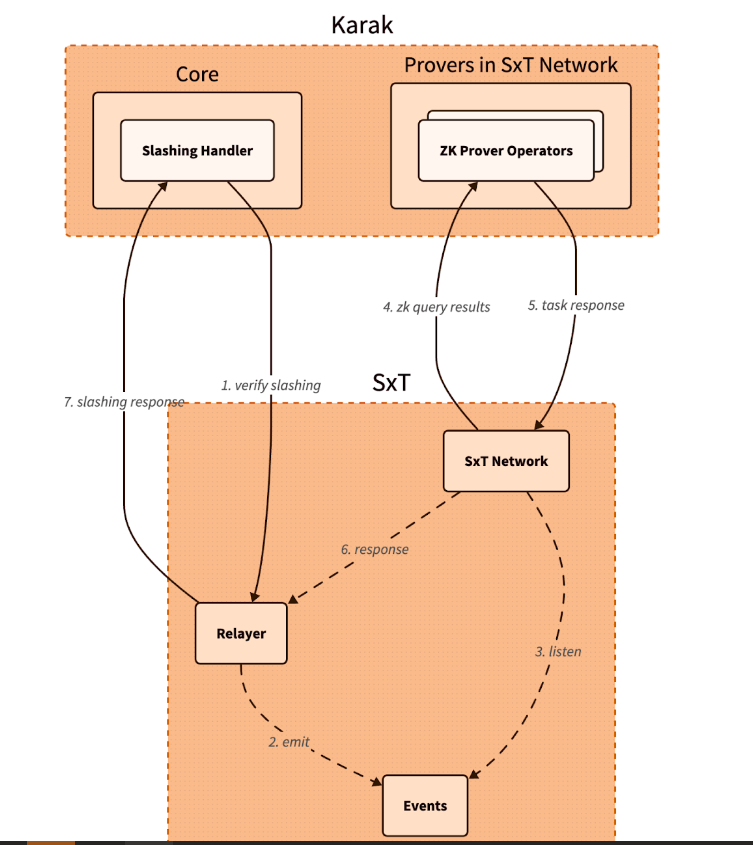
Additionally, Space and Time is developing its own DSS for blockchain data indexing. This service will allow community members to easily participate in the network by running indexing nodes. This is especially beneficial for applications that require high security and decentralization, such as decentralized data indexing.
The integration architecture follows a detailed and secure flow. When a Karak slashing contract needs to verify a SQL query, it calls the Space and Time relayer contract with the required SQL statement. This contract then emits an event with the query details, which is detected by operators in the Space and Time network.
These operators, responsible for indexing and monitoring DSS activities, validate the event and route the work to a verification operator who runs the query and generates the necessary ZK proof.
The result, along with a cryptographic commitment on the queried data, is sent to the relayer contract, which verifies and returns the data to the Karak cutter contract. This end-to-end process ensures that the data used in decision-making, such as determining penalties within the DSS, is accurate and reliable.
Karak’s mission is to provide universal security, but it also extends the capabilities of Space and Time to support multiple DSSs with their data indexing needs. As these technologies evolve, they are set to redefine the secure, decentralized computing landscape, making it more accessible and efficient for developers and enterprises alike. This integration represents a significant step towards a more secure and verifiable digital infrastructure in the blockchain space.
Website | X (Twitter) | Discord | Telegram
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
Cryptocurrency Payments: Should CFOs Consider This Ferrari-Approved Trend?

Iconic Italian luxury carmaker Ferrari has announced the expansion of its cryptocurrency payment system to its European dealer network.
The move, which follows a successful launch in North America less than a year ago, raises a crucial question for CFOs across industries: Is it time to consider accepting cryptocurrency as a form of payment for your business?
Ferrari’s move isn’t an isolated one. It’s part of a broader trend of companies embracing digital assets. As of 2024, we’re seeing a growing number of companies, from tech giants to traditional retailers, accepting cryptocurrencies.
This change is determined by several factors:
- Growing mainstream adoption of cryptocurrencies
- Growing demand from tech-savvy and affluent consumers
- Potential for faster and cheaper international transactions
- Desire to project an innovative brand image
Ferrari’s approach is particularly noteworthy. They have partnered with BitPay, a leading cryptocurrency payment processor, to allow customers to purchase vehicles using Bitcoin, Ethereum, and USDC. This satisfies their tech-savvy and affluent customer base, many of whom have large digital asset holdings.
Navigating Opportunities and Challenges
Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments illustrates several key opportunities for companies considering this move. First, it opens the door to new customer segments. By accepting cryptocurrency, Ferrari is targeting a younger, tech-savvy demographic—people who have embraced digital assets and see them as a legitimate form of value exchange. This strategy allows the company to connect with a new generation of affluent customers who may prefer to conduct high-value transactions in cryptocurrency.
Second, cryptocurrency adoption increases global reach. International payments, which can be complex and time-consuming with traditional methods, become significantly easier with cryptocurrency transactions. This can be especially beneficial for businesses that operate in multiple countries or deal with international customers, as it potentially reduces friction in cross-border transactions.
Third, accepting cryptocurrency positions a company as innovative and forward-thinking. In today’s fast-paced business environment, being seen as an early adopter of emerging technologies can significantly boost a brand’s image. Ferrari’s move sends a clear message that they are at the forefront of financial innovation, which can appeal to customers who value cutting-edge approaches.
Finally, there is the potential for cost savings. Traditional payment methods, especially for international transactions, often incur substantial fees. Cryptocurrency transactions, on the other hand, can offer lower transaction costs. For high-value purchases, such as luxury cars, these savings could be significant for both the business and the customer.
While the opportunities are enticing, accepting cryptocurrency payments also presents significant challenges that businesses must address. The most notable of these is volatility. Cryptocurrency values can fluctuate dramatically, sometimes within hours, posing potential risk to businesses that accept them as payment. Ferrari addressed this challenge by implementing a system that instantly converts cryptocurrency received into traditional fiat currencies, effectively mitigating the risk of value fluctuations.
Regulatory uncertainty is another major concern. The legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies is still evolving in many jurisdictions around the world. This lack of clear and consistent regulations can create compliance challenges for companies, especially those operating internationally. Companies must remain vigilant and adaptable as new laws and regulations emerge, which can be a resource-intensive process.
Implementation costs are also a significant obstacle. Integrating cryptocurrency payment systems often requires substantial investment in new technology infrastructure and extensive staff training. This can be especially challenging for small businesses or those with limited IT resources. The costs are not just financial; a significant investment of time is also required to ensure smooth implementation and operation.
Finally, security concerns loom large in the world of cryptocurrency transactions. While blockchain technology offers some security benefits, cryptocurrency transactions still require robust cybersecurity measures to protect against fraud, hacks, and other malicious activity. Businesses must invest in robust security protocols and stay up-to-date on the latest threats and protections, adding another layer of complexity and potential costs to accepting cryptocurrency payments.
Strategic Considerations for CFOs
If you’re thinking of following in Ferrari’s footsteps, here are the key factors to consider:
- Risk Assessment: Carefully evaluate potential risks to your business, including financial, regulatory, and reputational risks.
- Market Analysis: Evaluate whether your customer base is significantly interested in using cryptocurrencies for payments.
- Technology Infrastructure: Determine the costs and complexities of implementing a cryptographic payment system that integrates with existing financial processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that cryptocurrency acceptance is in line with local regulations in all markets you operate in. Ferrari’s gradual rollout demonstrates the importance of this consideration.
- Financial Impact: Analyze how accepting cryptocurrency could impact your cash flow, accounting practices, and financial reporting.
- Partnership Evaluation: Consider partnering with established crypto payment processors to reduce risk and simplify implementation.
- Employee Training: Plan comprehensive training to ensure your team is equipped to handle cryptocurrency transactions and answer customer questions.
While Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments is exciting, it’s important to consider this trend carefully.
A CFO’s decision to adopt cryptocurrency as a means of payment should be based on a thorough analysis of your company’s specific needs, risk tolerance, and strategic goals. Cryptocurrency payments may not be right for every business, but for some, they could provide a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Remember that the landscape is rapidly evolving. Stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. Whether you decide to accelerate your crypto engines now or wait in the pit, keeping this payment option on your radar is critical to navigating the future of business transactions.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
Sign up to receive your daily business insights
Tech
Bitcoin Tumbles as Crypto Market Selloff Mirrors Tech Stocks’ Plunge
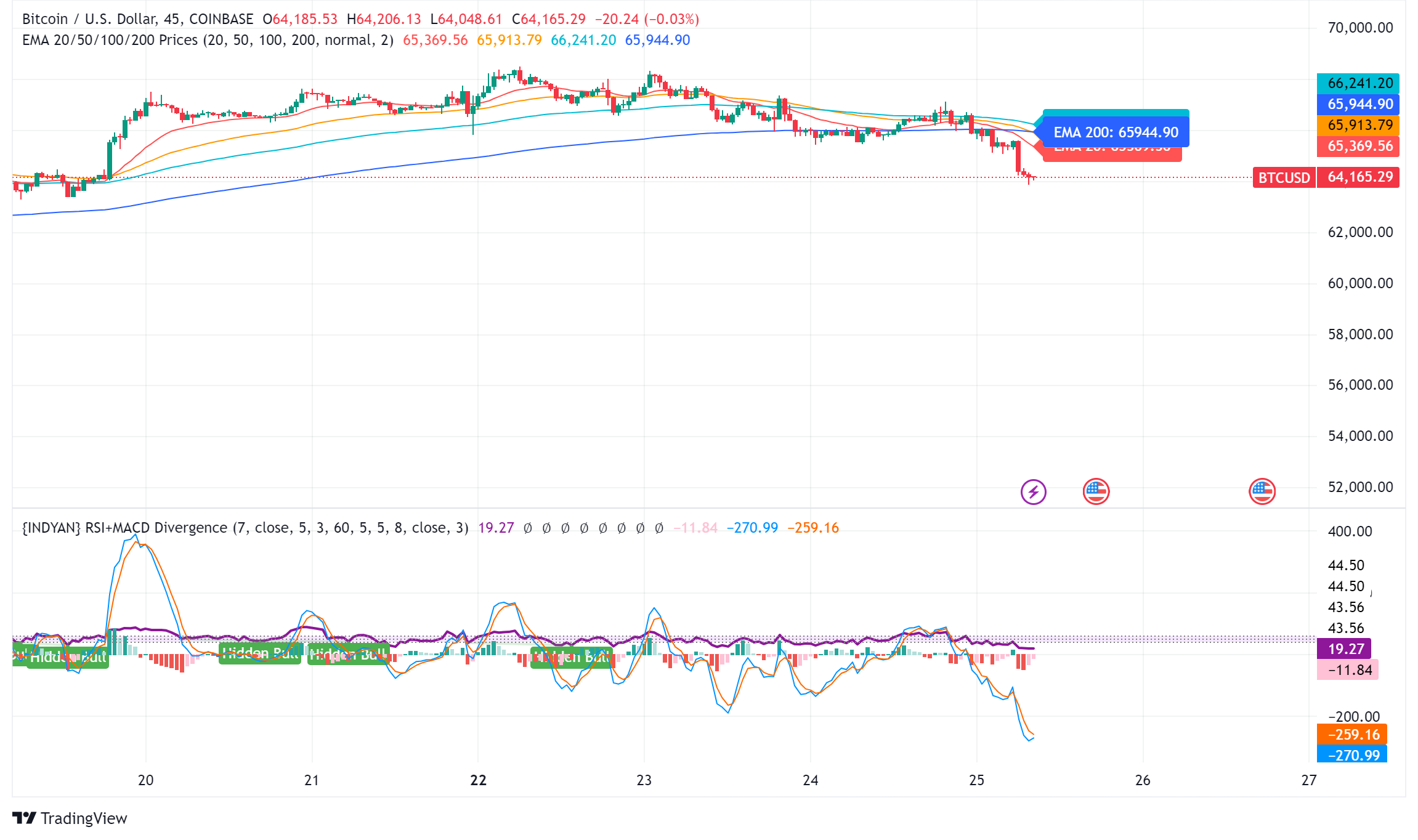
The world’s largest cryptocurrency, Bitcoin (BTC), suffered a significant price decline on Wednesday, falling below $65,000. The decline coincides with a broader market sell-off that has hit technology stocks hard.
Cryptocurrency Liquidations Hit Hard
CoinGlass data reveals a surge in long liquidations in the cryptocurrency market over the past 24 hours. These liquidations, totaling $220.7 million, represent forced selling of positions that had bet on price increases. Bitcoin itself accounted for $14.8 million in long liquidations.
Ethereum leads the decline
Ethereal (ETH), the second-largest cryptocurrency, has seen a steeper decline than Bitcoin, falling nearly 8% to trade around $3,177. This decline mirrors Bitcoin’s price action, suggesting a broader market correction.
Cryptocurrency market crash mirrors tech sector crash
The cryptocurrency market decline appears to be linked to the significant losses seen in the U.S. stock market on Wednesday. Stock market listing The index, heavily weighted toward technology stocks, posted its sharpest decline since October 2022, falling 3.65%.
Analysts cite multiple factors
Several factors may have contributed to the cryptocurrency market crash:
- Tech earnings are underwhelming: Earnings reports from tech giants like Alphabet are disappointing (Google(the parent company of), on Tuesday, triggered a sell-off in technology stocks with higher-than-expected capital expenditures that could have repercussions on the cryptocurrency market.
- Changing Political Landscape: The potential impact of the upcoming US elections and changes in Washington’s policy stance towards cryptocurrencies could influence investor sentiment.
- Ethereal ETF Hopes on the line: While bullish sentiment around a potential U.S. Ethereum ETF initially boosted the market, delays or rejections could dampen enthusiasm.
Analysts’ opinions differ
Despite the short-term losses, some analysts remain optimistic about Bitcoin’s long-term prospects. Singapore-based cryptocurrency trading firm QCP Capital believes Bitcoin could follow a similar trajectory to its post-ETF launch all-time high, with Ethereum potentially converging with its previous highs on sustained institutional interest.
Rich Dad Poor Dad Author’s Prediction
Robert Kiyosaki, author of the best-selling Rich Dad Poor Dad, predicts a potential surge in the price of Bitcoin if Donald Trump is re-elected as US president. He predicts a surge to $105,000 per coin by August 2025, fueled by a weaker dollar that is set to boost US exports.
BTC/USD Technical Outlook
Bitcoin price is currently trading below key support levels, including the $65,500 level and the 100 hourly moving average. A break below the $64,000 level could lead to further declines towards the $63,200 support zone. However, a recovery above the $65,500 level could trigger another increase in the coming sessions.
-

 Videos1 month ago
Videos1 month agoAbsolutely massive: the next higher Bitcoin leg will shatter all expectations – Tom Lee
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoVolta Finance Limited – Director/PDMR Shareholding
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoModiv Industrial to release Q2 2024 financial results on August 6
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoApple to report third-quarter earnings as Wall Street eyes China sales
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoNumber of Americans filing for unemployment benefits hits highest level in a year
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoInventiva reports 2024 First Quarter Financial Information¹ and provides a corporate update
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoLeeds hospitals trust says finances are “critical” amid £110m deficit
-

 Markets1 year ago
Markets1 year agoWhale Investments in Bitcoin Hit $100 Billion in 2024, Fueling Insane Investor Optimism ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 DeFi1 year ago
DeFi1 year ago🏴☠️ Pump.Fun operated by Insider Exploit
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year ago$1,000,000 worth of BTC in 2025! Get ready for an UNPRECEDENTED PRICE EXPLOSION – Jack Mallers
-
 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoABSOLUTELY HUGE: Bitcoin is poised for unabated exponential growth – Mark Yusko and Willy Woo
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoBlockDAG ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Review: Is It the Next Big Thing in Cryptocurrency? 5 questions answered















