Tech
Definition and How It Works
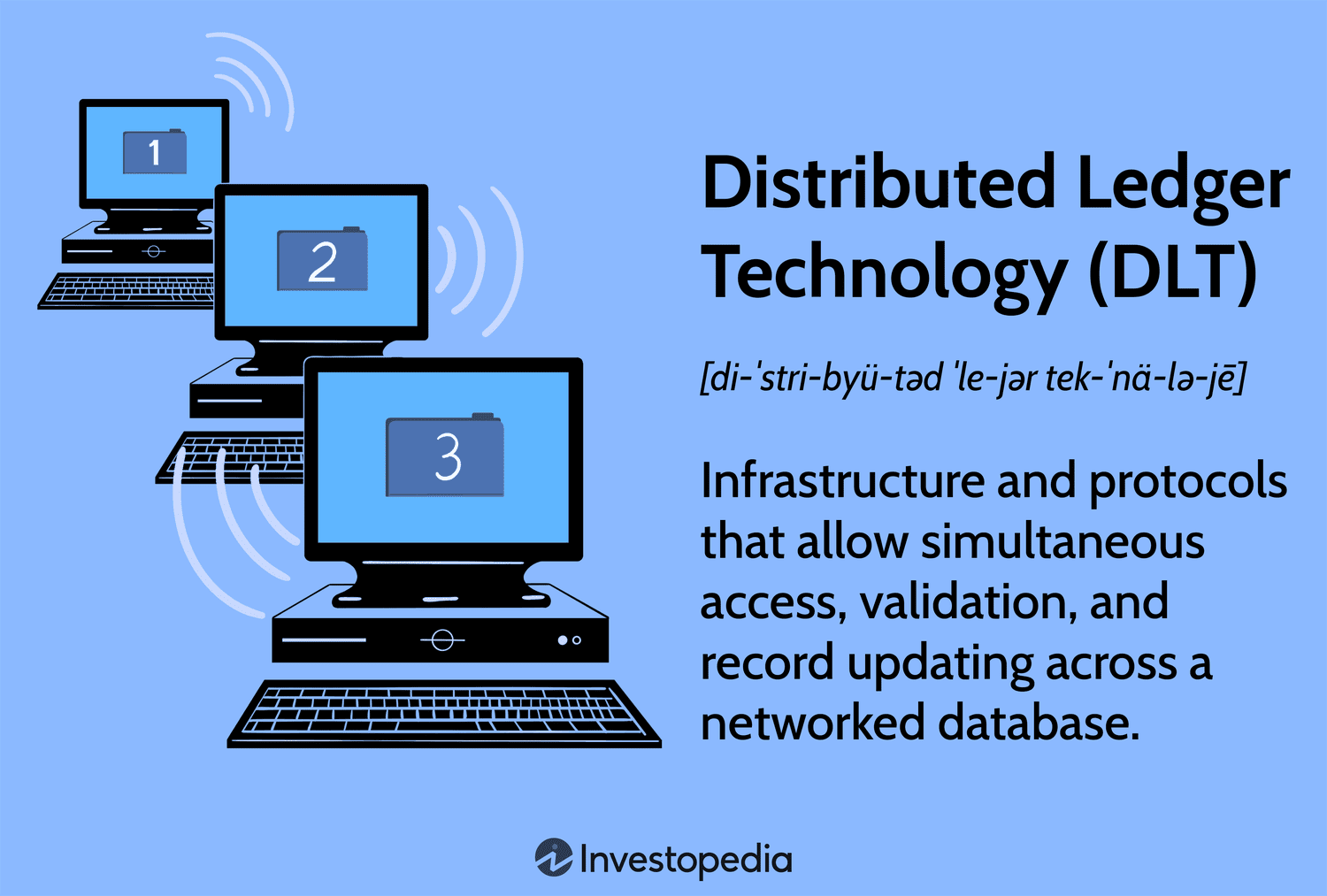
What Is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is the technological infrastructure and protocols that allow simultaneous access, validation, and record updating across a networked database. DLT is the technology blockchains are created from, and the infrastructure allows users to view any changes and who made them, reduces the need to audit data, ensures data is reliable, and only provides access to those that need it.
Key Takeaways
- Distributed ledgers are maintained by a network of nodes, each of which has a copy of the ledger, validates the information, and helps reach a consensus about its accuracy.
- Distributed ledgers have been around for decades but have become more well-known, researched, used, and developed since Bitcoin was introduced.
- Distributed ledgers can be used in nearly every industry where data is collected and used.
- All blockchains are distributed ledgers, but not all distributed ledgers are blockchains.
- Though DLT enhances accountability, security, and accessibility, it is still complex and difficult to scale.
History of Distributed Ledgers
Distributed computing is not new—businesses and governments have been using the concept for several decades. In the 1990s, it became possible for multiple computers and users in different locations to solve problems and return the solutions to a central location.
Advances in data science, computing, software, hardware, and other technologies have made ledgers much more capable. Improved connectivity through intranet and internet protocols allowed for much more data to be collected, analyzed, and used. However, because there can now be many users with access to data, it is necessary to have someone verify the changes.
Computer and data scientists developed programs that reduced the need for auditing data. These programs used automation and data encryption techniques to verify database transactions or changes in a database’s state. This is called consensus—the act of automated majority agreement on transaction validity, where a transaction is simply a change made to a database’s state.
Distributed ledgers evolved into scalable and programmable platforms, as seen in Ethereum and HyperLedger, where solutions can be created to use a database, or ledger, for everything from tokenizing physical assets to streamlining manufacturing and other business processes.
How Distributed Ledger Technology Works
DLTs allow information to be stored securely and accurately using cryptography. The data can be accessed using “keys” and cryptographic signatures. Once the information is stored, it can become an immutable database; the rules of the network, written into the coding of the database programming, govern the ledger.
If something is immutable, it is unable to be changed. Distributed ledgers are only immutable if they are programmed to be that way. Blockchains are immutable because they are decentralized and cryptographically enhanced public ledgers.
Because they are decentralized, private, and encrypted, distributed ledgers are less prone to cybercrime, as all the copies stored across the network need to be attacked simultaneously for the attack to be successful. Additionally, the peer-to-peer sharing and updating of records make the whole process much faster, more effective, and cheaper.
Every device on a distributed ledger network stores a copy of the ledger. These devices are called nodes—a network can have any number of nodes. Any changes to the ledger, such as moving data from one block to another, are recorded across all nodes. Because each node has a copy of the ledger, each one publishes its version with the latest transactions.
If the network reaches a consensus about the validity of the latest ledger, the transactions are finalized, encrypted, and used as a basis for the following transactions. This is how blockchains develop—each block contains encrypted information about the proceeding block, which makes them impossible to change.
Industries Using Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed ledgers are created for many different purposes, but one of the most used ways is as a platform for others to scale and use. One of the more well-known distributed ledgers is Hyperledger Fabric. It is a modular and scalable DLT platform several businesses have used to create solutions that span many industries. Some industries that have implemented DLT solutions include aviation, education, healthcare, insurance, manufacturing, transportation, and utilities.
Supply chains can benefit greatly from DLT. Many factors make them inefficient, inaccurate, and susceptible to corruption or losses. Fujitsu, a global data and information technology company, has designed distributed ledger technology to enhance supply chain transparency and fraud prevention by securing and tracking data.
Fujitsu’s Rice Exchange was created to trade rice, ensuring data regarding sources, prices, insurance, shipping, and settlement are recorded on the ledger. Anyone involved can look at any data and find accurate information regarding the entire process because it cannot be changed. All data is entered and secured automatically by the platform—it will eventually provide tracking information for rice shipping containers as it is shipped to its final destination.
Uses of Distributed Ledger Technology
Aside from specific industries, there are also specific situations where DLT solutions have proven to add value. Some examples of specific DLT uses include:
- Record transactions: DLT enables secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions without the need for a central authority. As DLT is a ledger, it records inputs and outputs. Though this naturally lends itself to financial records, DLT can record any type of transaction, not just financially based ones.
- Secure identities: DLT can be used to create a secure and tamper-proof digital identity for individuals, as the technology can provide a reliable way to verify identities and prevent identity theft.
- Collect votes: DLT can be used to create a secure and transparent voting system that can prevent voter fraud and ensure the integrity of the voting process. As mentioned above, as transactions (financial or non-financial) are recorded, a transparent, immutable, open ledger of interactions with users is saved. This enhances the equity and believability of a collection of opinions.
- Enter contracts: DLT allows for smart contracts, agreements that automatically execute or complete based on prevailing conditions. For example, an insurance claim may automatically release funds once the claim has been processed. This limits error and DLTs make it more difficult for precarious activity by bad actors.
- Demonstrate ownership: DLT can be used to record property transactions, creating a tamper-proof and transparent record of ownership and transfer of property. Though there are some limitations on translating real-world ownership of physical assets to a distributed ledger, the ledger may be able to convey an unchangeable source of truth regarding ownership.
DLT may also be referred to as a shared ledger as it requires a ledger to be shared across a peer-to-peer computer network.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Distributed Ledger Technology
Pros of DLT
DLT holds many benefits over more traditional centralized ledger systems. Because DLT is a decentralized system, there is no central point of control or failure. This makes DLT more resilient to attacks and less vulnerable to system-wide failures. Also, because DLT uses cryptographic algorithms to secure data, it is nearly impossible to tamper with or forge records. This enhances the trustworthiness of the data and reduces the risk of fraud.
DLT allows for transparent access to data and transactions, allowing all users greater visibility into the operations of the system. This may lead to greater buy-in from users due to transparency and accountability of records.
DLT can streamline processes by removing intermediaries and automating transactions through smart contracts. Because smart contracts may automatically execute when contract conditions are met, there may be less need for human interaction or administration. This can reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Last, DLT can enable greater financial inclusion. Some people may not have access to traditional banking services. As DLT often relies only on an internet connection, individuals who would be otherwise limited may have access to a greater range of services. This extends to the use of different platforms and networks via interoperability.
Cons of DLT
Due to DLT’s infancy, there are still considerable downsides to the technology. DLT is still complex and difficult to implement and maintain. Leveraging the solution often requires specialized knowledge and expertise, especially to implement.
DLT can struggle with scalability as the number of participants and transactions increases. As a result, DLT processes may lead to slower processing capabilities or higher use costs. In addition, some DLTs such as Bitcoin require a significant amount of energy to maintain the network and process transactions. This can have negative environmental impacts.
As seen by the actions of bad actors, the lack of regulation and standardization in the blockchain industry (blockchains are derived from DLT) can lead to risk for users and investors. By extension, DLT requires widespread adoption to be effective, and many industries and organizations may be hesitant to adopt new technologies due to these security concerns.
Distributed ledgers might be immutable, but this benefit also comes with a significant downside—if mistakes are made, they cannot be changed unless there are users with permission to do so. In a public DLT like the Bitcoin blockchain, this can be problematic. For instance, if a user typed an erroneous address in their wallet and sent the wrong person some Bitcoin, they cannot reverse the transaction.
Pros
-
Spreads systematic risk around, minimizing the risk of a single point of failure
-
Has greater security due to cryptographic algorithms
-
Allows for transparency and visibility into operations
-
May prove to be more efficient due to smart contract automation
-
Offers individuals with limited access to traditional systems potentially greater capabilities
Cons
-
Is more complex compared to traditional ledger solutions
-
Can require higher energy consumption for operation
-
May have difficult scaling as more users/transactions occur
-
Some applications remain risky due to lack of regulation
-
May prove to be difficult to reverse fraudulent or erroneous activity
Why Distribute Ledger Technology Is Important
DLT is important because it has the potential to transform how information is recorded, stored, and distributed. The importance is often cited across three pillars: security, transparency, and accessibility.
Security
Traditional ledger technology often has a central point of control, with one single entity often in charge of the ledger. DLT makes the ledger more resilient to attacks and less vulnerable to system-wide failures. As DLT uses cryptographic algorithms to secure data, it also makes it more difficult to tamper with or forge records.
Consider a traditional banking system where a banker is the central point in ensuring your transaction is recorded correctly. In contrast, consider a DLT solution built on a consensus mechanism where all distributed ledgers must be in agreement about how a transaction is recorded. This validation of transactions allows greater trust among users and removes the power an individual might have to alter data.
Transparency
Centralized, traditional ledgers often restrict access to specific individuals. Though this still holds value for sensitive information, there are many use cases where it is more beneficial for all when data and information are broadly distributed and transparent. Consider the example above of voting; having digitally distributed, undisputable, verifiable records of voting may enhance the believability of results.
DLT is also important as it holds the theory of reducing fraud and increasing accountability in the long term. Note how all transactions within a DLT system are able to be viewed by anyone with access to the DLT. The information may be “audited” by anyone at any time, potentially demotivating bad actors from entering into nefarious activity in such a public sphere.
Accessibility
Last, DLT may eventually be critically important to developing and emerging countries or regions where centralized technologies are limited. Think about the banking limitations of different countries around the world. DLT boasts the ability to store and record transactions using only a network connection as opposed to a very niche (and expensive) connection, such as a bank account at a specific bank.
As DLT is a relatively new technology that is still being explored and developed, this presents opportunities for innovation and the creation of new applications and use cases. In general, because of the ease of being to access DLT solutions, there are many positive implications on the broad public being able to communally access a shared network with often fewer bureaucratic hurdles to meet prior to access.
Distributed Ledger Technology Consensus Mechanisms
A central facet of DLT is how transactions are “approved” when consensus needs to be reached among a disparate user base. Without a universally-agreed system of how items are accepted within the DLT, users of the DLT would be unable to universally agree on how items to include and what items should be excluded.
This process of reviewing transactions is called a consensus mechanism, and a DLT may leverage any of the following processes. Note that consensus mechanisms are constantly evolving, and only several of the more common approaches are listed below:
- Proof of Work (PoW): In PoW, miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This type of consensus mechanism requires computational power, making it a less environmentally friendly method. The concept behind PoW is that miners must financially invest and commit resources to approve transactions, so they are incentivized to be “good actors.”
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In PoS, validators hold a stake in the network and are chosen to validate transactions based on the amount of the stake they hold. Seen as a more environmentally friendly option, it is very expensive to become a full validator and earn rewards.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): DPoS is a variant of proof of stake where the network selects a limited number of validators to validate transactions. This variation reduces the computational resources required to secure the network. In many ways, a DPoS system is seen as a more democratic means of selecting approvers and, in some instances, might offer better scalability.
Distributed Ledgers vs. Blockchain
There are several key factors that distinguish blockchain from distributed ledgers. In general, blockchain is a specific type of DLT. DLTs may take various forms, while a blockchain uses one specific infrastructure that uses a linear system of blocks to record and verify information.
Blockchains often leverage a proof of work or proof of stake consensus mechanism, whereas a DLT has a much broader range of mechanisms available. In addition, DLTs are often more broadly used across industries as they can be leveraged for broader problems. Blockchain has historically been most associated with the financial sector as a means of recording a payment system. The security behind either may also vary, with blockchain having a very defined set of criteria within the DLT realm.
Blockchain
-
Data is stored in chained files called “blocks”
-
Always encrypted
-
Generally public and permissionless, but some are permissioned
-
Always immutable
What Is Another Word For Distributed Ledger?
You might hear a distributed ledger called a share ledger.
Are DLT and Blockchain the Same?
All blockchains are distributed ledgers (DLs), but the opposite is not true—blockchains are derived from DLs.
What Is the Difference Between a Distibuted Ledger and a Centralized Ledger?
A centralized ledger is a database stored in a centralized location. It could be hosted by an individual, group, or organization that maintains it. A distributed ledger is a database where a copy is distributed, shared, and automatically synchronized.
What Is Meaning of DLT?
Distributed ledger technology is the concept of using modern networking systems, hardware, and programming to distribute copies of a database to multiple nodes that synchronize it to maintain it.
The Bottom Line
Distributed ledger technology uses databases stored on separate, connected devices in a network to ensure data accuracy and security. Blockchains evolved from distributed ledgers to address growing concerns that too many third parties are involved in too many transactions.
Distributed ledger technology is becoming necessary in modern businesses and enterprises that need to ensure accuracy in financial reporting, manage supply chains, prevent fraud, and identify inefficiencies. It has many more use cases in time-consuming and costly business activities.
Tech
Harvard Alumni, Tech Moguls, and Best-Selling Authors Drive Nearly $600 Million in Pre-Order Sales

BlockDAG Network’s history is one of innovation, perseverance, and a vision to push the boundaries of blockchain technology. With Harvard alumni, tech moguls, and best-selling authors at the helm, BlockDAG is rewriting the rules of the cryptocurrency game.
CEO Antony Turner, inspired by the successes and shortcomings of Bitcoin and Ethereum, says, “BlockDAG leverages existing technology to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.” This powerhouse team has led a staggering 1,600% price increase in 20 pre-sale rounds, raising over $63.9 million. The secret? Unparalleled expertise and a bold vision for the future of blockchain.
Let’s dive into BlockDAG’s success story and find out what the future holds for this cryptocurrency.
The Origin: Why BlockDAG Was Created
In a recent interview, BlockDAG CEO Antony Turner perfectly summed up why the market needs BlockDAG’s ongoing revolution. He said:
“The creation of BlockDAG was inspired by Bitcoin and Ethereum, their successes and their shortcomings.
If you look at almost any new technology, it is very rare that the first movers remain at the forefront forever. Later incumbents have a huge advantage in entering a market where the need has been established and the technology is no longer cutting edge.
BlockDAG has done just that: our innovation is incorporating existing technology to provide a better solution, allowing us to push the boundaries of speed, security, and decentralization.”
The Present: How Far Has BlockDAG Come?
BlockDAG’s presale is setting new benchmarks in the cryptocurrency investment landscape. With a stunning 1600% price increase over 20 presale lots, it has already raised over $63.9 million in capital, having sold over 12.43 billion BDAG coins.
This impressive performance underscores the overwhelming confidence of investors in BlockDAG’s vision and leadership. The presale attracted over 20,000 individual investors, with the BlockDAG community growing exponentially by the hour.

These monumental milestones have been achieved thanks to the unparalleled skills, experience and expertise of BlockDAG’s management team:
Antony Turner – Chief Executive Officer
Antony Turner, CEO of BlockDAG, has over 20 years of experience in the Fintech, EdTech, Travel and Crypto industries. He has held senior roles at SPIRIT Blockchain Capital and co-founded Axona-Analytics and SwissOne. Antony excels in financial modeling, business management and scaling growth companies, with expertise in trading, software, IoT, blockchain and cryptocurrency.
Director of Communications
Youssef Khaoulaj, CSO of BlockDAG, is a Smart Contract Auditor, Metaverse Expert, and Red Team Hacker. He ensures system security and disaster preparedness, and advises senior management on security issues.
advisory Committee
Steven Clarke-Martin, a technologist and consultant, excels in enterprise technology, startups, and blockchain, with a focus on DAOs and smart contracts. Maurice Herlihy, a Harvard and MIT graduate, is an award-winning computer scientist at Brown University, with experience in distributed computing and consulting roles, most notably at Algorand.
The Future: Becoming the Cryptocurrency with the Highest Market Cap in the World
Given its impressive track record and a team of geniuses working tirelessly behind the scenes, BlockDAG is quickly approaching the $600 million pre-sale milestone. This crypto powerhouse will soon enter the top 30 cryptocurrencies by market cap.
Currently trading at $0.017 per coin, BlockDAG is expected to hit $1 million in the coming months, with the potential to hit $30 per coin by 2030. Early investors have already enjoyed a 1600% ROI by batch 21, fueling a huge amount of excitement around BlockDAG’s presale. The platform is seeing significant whale buying, and demand is so high that batch 21 is almost sold out. The upcoming batch is expected to drive prices even higher.

Invest in BlockDAG Pre-Sale Now:
Pre-sale: https://purchase.blockdag.network
Website: https://blockdag.network
Telegram: https://t.me/blockDAGnetwork
Discord: Italian: https://discord.gg/Q7BxghMVyu
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
How Karak’s Latest Tech Integration Could Make Data Breaches Obsolete

- Space and Time uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure secure and tamper-proof data processing for smart contracts and enterprises.
- The integration facilitates faster development and deployment of Distributed Secure Services (DSS) on the Karak platform.
Karak, a platform known for its strong security capabilities, is enhancing its Distributed Secure Services (DSS) by integrating Space and Time as a zero-knowledge (ZK) coprocessor. This move is intended to strengthen trustless operations across its network, especially in slashing and rewards mechanisms.
Space and Time is a verifiable processing layer that uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure that computations on decentralized data warehouses are secure and untampered with. This system enables smart contracts, large language models (LLMs), and enterprises to process data without integrity concerns.
The integration with Karak will enable the platform to use Proof of SQL, a new ZK-proof approach developed by Space and Time, to confirm that SQL query results are accurate and have not been tampered with.
One of the key features of this integration is the enhancement of DSS on Karak. DSS are decentralized services that use re-staked assets to secure the various operations they provide, from simple utilities to complex marketplaces. The addition of Space and Time technology enables faster development and deployment of these services, especially by simplifying slashing logic, which is critical to maintaining security and trust in decentralized networks.
Additionally, Space and Time is developing its own DSS for blockchain data indexing. This service will allow community members to easily participate in the network by running indexing nodes. This is especially beneficial for applications that require high security and decentralization, such as decentralized data indexing.
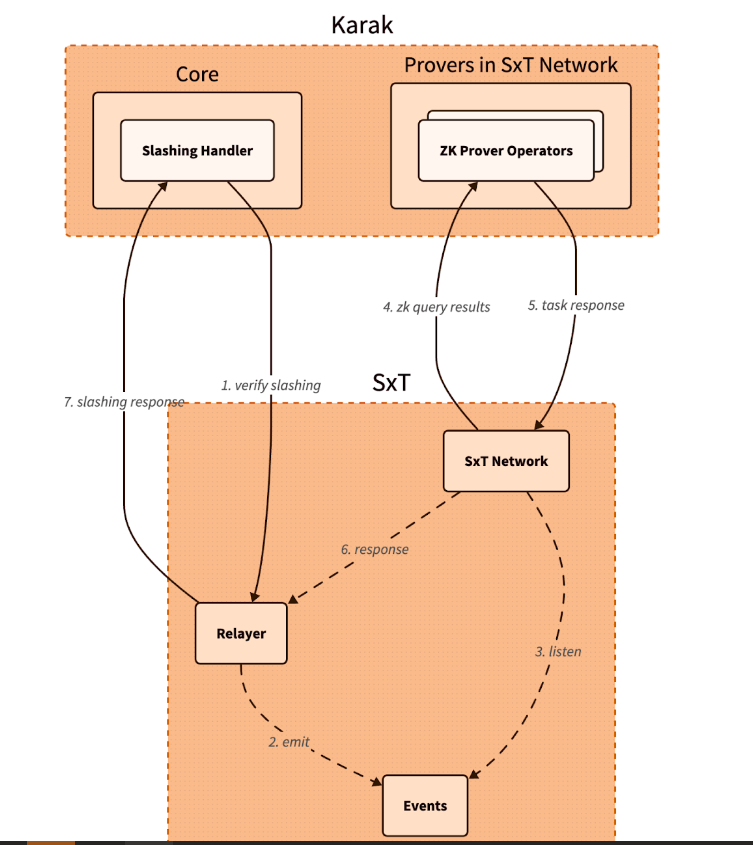
The integration architecture follows a detailed and secure flow. When a Karak slashing contract needs to verify a SQL query, it calls the Space and Time relayer contract with the required SQL statement. This contract then emits an event with the query details, which is detected by operators in the Space and Time network.
These operators, responsible for indexing and monitoring DSS activities, validate the event and route the work to a verification operator who runs the query and generates the necessary ZK proof.
The result, along with a cryptographic commitment on the queried data, is sent to the relayer contract, which verifies and returns the data to the Karak cutter contract. This end-to-end process ensures that the data used in decision-making, such as determining penalties within the DSS, is accurate and reliable.
Karak’s mission is to provide universal security, but it also extends the capabilities of Space and Time to support multiple DSSs with their data indexing needs. As these technologies evolve, they are set to redefine the secure, decentralized computing landscape, making it more accessible and efficient for developers and enterprises alike. This integration represents a significant step towards a more secure and verifiable digital infrastructure in the blockchain space.
Website | X (Twitter) | Discord | Telegram
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Tech
Cryptocurrency Payments: Should CFOs Consider This Ferrari-Approved Trend?

Iconic Italian luxury carmaker Ferrari has announced the expansion of its cryptocurrency payment system to its European dealer network.
The move, which follows a successful launch in North America less than a year ago, raises a crucial question for CFOs across industries: Is it time to consider accepting cryptocurrency as a form of payment for your business?
Ferrari’s move isn’t an isolated one. It’s part of a broader trend of companies embracing digital assets. As of 2024, we’re seeing a growing number of companies, from tech giants to traditional retailers, accepting cryptocurrencies.
This change is determined by several factors:
- Growing mainstream adoption of cryptocurrencies
- Growing demand from tech-savvy and affluent consumers
- Potential for faster and cheaper international transactions
- Desire to project an innovative brand image
Ferrari’s approach is particularly noteworthy. They have partnered with BitPay, a leading cryptocurrency payment processor, to allow customers to purchase vehicles using Bitcoin, Ethereum, and USDC. This satisfies their tech-savvy and affluent customer base, many of whom have large digital asset holdings.
Navigating Opportunities and Challenges
Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments illustrates several key opportunities for companies considering this move. First, it opens the door to new customer segments. By accepting cryptocurrency, Ferrari is targeting a younger, tech-savvy demographic—people who have embraced digital assets and see them as a legitimate form of value exchange. This strategy allows the company to connect with a new generation of affluent customers who may prefer to conduct high-value transactions in cryptocurrency.
Second, cryptocurrency adoption increases global reach. International payments, which can be complex and time-consuming with traditional methods, become significantly easier with cryptocurrency transactions. This can be especially beneficial for businesses that operate in multiple countries or deal with international customers, as it potentially reduces friction in cross-border transactions.
Third, accepting cryptocurrency positions a company as innovative and forward-thinking. In today’s fast-paced business environment, being seen as an early adopter of emerging technologies can significantly boost a brand’s image. Ferrari’s move sends a clear message that they are at the forefront of financial innovation, which can appeal to customers who value cutting-edge approaches.
Finally, there is the potential for cost savings. Traditional payment methods, especially for international transactions, often incur substantial fees. Cryptocurrency transactions, on the other hand, can offer lower transaction costs. For high-value purchases, such as luxury cars, these savings could be significant for both the business and the customer.
While the opportunities are enticing, accepting cryptocurrency payments also presents significant challenges that businesses must address. The most notable of these is volatility. Cryptocurrency values can fluctuate dramatically, sometimes within hours, posing potential risk to businesses that accept them as payment. Ferrari addressed this challenge by implementing a system that instantly converts cryptocurrency received into traditional fiat currencies, effectively mitigating the risk of value fluctuations.
Regulatory uncertainty is another major concern. The legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies is still evolving in many jurisdictions around the world. This lack of clear and consistent regulations can create compliance challenges for companies, especially those operating internationally. Companies must remain vigilant and adaptable as new laws and regulations emerge, which can be a resource-intensive process.
Implementation costs are also a significant obstacle. Integrating cryptocurrency payment systems often requires substantial investment in new technology infrastructure and extensive staff training. This can be especially challenging for small businesses or those with limited IT resources. The costs are not just financial; a significant investment of time is also required to ensure smooth implementation and operation.
Finally, security concerns loom large in the world of cryptocurrency transactions. While blockchain technology offers some security benefits, cryptocurrency transactions still require robust cybersecurity measures to protect against fraud, hacks, and other malicious activity. Businesses must invest in robust security protocols and stay up-to-date on the latest threats and protections, adding another layer of complexity and potential costs to accepting cryptocurrency payments.
Strategic Considerations for CFOs
If you’re thinking of following in Ferrari’s footsteps, here are the key factors to consider:
- Risk Assessment: Carefully evaluate potential risks to your business, including financial, regulatory, and reputational risks.
- Market Analysis: Evaluate whether your customer base is significantly interested in using cryptocurrencies for payments.
- Technology Infrastructure: Determine the costs and complexities of implementing a cryptographic payment system that integrates with existing financial processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that cryptocurrency acceptance is in line with local regulations in all markets you operate in. Ferrari’s gradual rollout demonstrates the importance of this consideration.
- Financial Impact: Analyze how accepting cryptocurrency could impact your cash flow, accounting practices, and financial reporting.
- Partnership Evaluation: Consider partnering with established crypto payment processors to reduce risk and simplify implementation.
- Employee Training: Plan comprehensive training to ensure your team is equipped to handle cryptocurrency transactions and answer customer questions.
While Ferrari’s adoption of cryptocurrency payments is exciting, it’s important to consider this trend carefully.
A CFO’s decision to adopt cryptocurrency as a means of payment should be based on a thorough analysis of your company’s specific needs, risk tolerance, and strategic goals. Cryptocurrency payments may not be right for every business, but for some, they could provide a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Remember that the landscape is rapidly evolving. Stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. Whether you decide to accelerate your crypto engines now or wait in the pit, keeping this payment option on your radar is critical to navigating the future of business transactions.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
Sign up to receive your daily business insights
Tech
Bitcoin Tumbles as Crypto Market Selloff Mirrors Tech Stocks’ Plunge
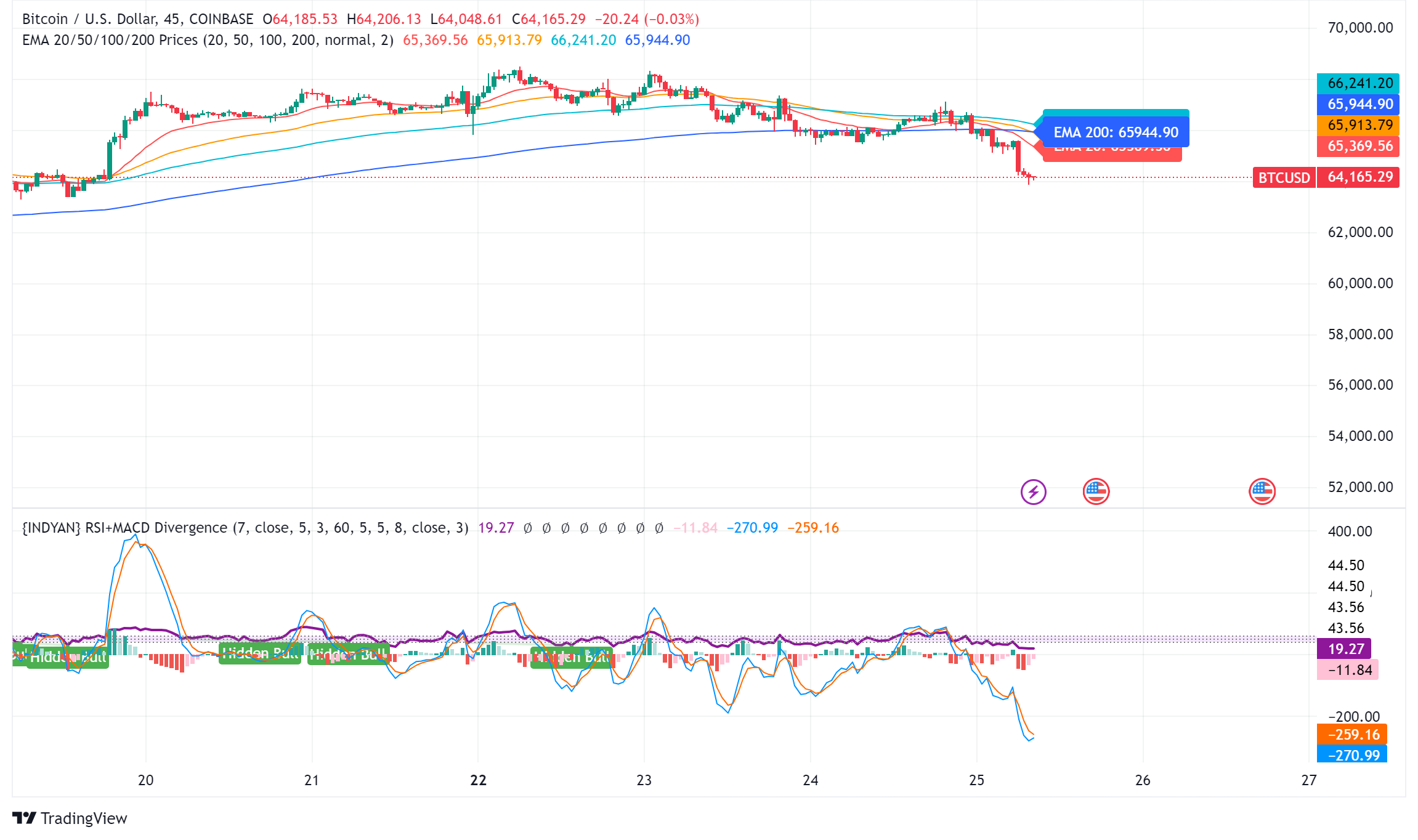
The world’s largest cryptocurrency, Bitcoin (BTC), suffered a significant price decline on Wednesday, falling below $65,000. The decline coincides with a broader market sell-off that has hit technology stocks hard.
Cryptocurrency Liquidations Hit Hard
CoinGlass data reveals a surge in long liquidations in the cryptocurrency market over the past 24 hours. These liquidations, totaling $220.7 million, represent forced selling of positions that had bet on price increases. Bitcoin itself accounted for $14.8 million in long liquidations.
Ethereum leads the decline
Ethereal (ETH), the second-largest cryptocurrency, has seen a steeper decline than Bitcoin, falling nearly 8% to trade around $3,177. This decline mirrors Bitcoin’s price action, suggesting a broader market correction.
Cryptocurrency market crash mirrors tech sector crash
The cryptocurrency market decline appears to be linked to the significant losses seen in the U.S. stock market on Wednesday. Stock market listing The index, heavily weighted toward technology stocks, posted its sharpest decline since October 2022, falling 3.65%.
Analysts cite multiple factors
Several factors may have contributed to the cryptocurrency market crash:
- Tech earnings are underwhelming: Earnings reports from tech giants like Alphabet are disappointing (Google(the parent company of), on Tuesday, triggered a sell-off in technology stocks with higher-than-expected capital expenditures that could have repercussions on the cryptocurrency market.
- Changing Political Landscape: The potential impact of the upcoming US elections and changes in Washington’s policy stance towards cryptocurrencies could influence investor sentiment.
- Ethereal ETF Hopes on the line: While bullish sentiment around a potential U.S. Ethereum ETF initially boosted the market, delays or rejections could dampen enthusiasm.
Analysts’ opinions differ
Despite the short-term losses, some analysts remain optimistic about Bitcoin’s long-term prospects. Singapore-based cryptocurrency trading firm QCP Capital believes Bitcoin could follow a similar trajectory to its post-ETF launch all-time high, with Ethereum potentially converging with its previous highs on sustained institutional interest.
Rich Dad Poor Dad Author’s Prediction
Robert Kiyosaki, author of the best-selling Rich Dad Poor Dad, predicts a potential surge in the price of Bitcoin if Donald Trump is re-elected as US president. He predicts a surge to $105,000 per coin by August 2025, fueled by a weaker dollar that is set to boost US exports.
BTC/USD Technical Outlook
Bitcoin price is currently trading below key support levels, including the $65,500 level and the 100 hourly moving average. A break below the $64,000 level could lead to further declines towards the $63,200 support zone. However, a recovery above the $65,500 level could trigger another increase in the coming sessions.
-

 News9 months ago
News9 months agoModiv Industrial to release Q2 2024 financial results on August 6
-

 News9 months ago
News9 months agoVolta Finance Limited – Director/PDMR Shareholding
-

 News9 months ago
News9 months agoApple to report third-quarter earnings as Wall Street eyes China sales
-

 News9 months ago
News9 months agoNumber of Americans filing for unemployment benefits hits highest level in a year
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoInventiva reports 2024 First Quarter Financial Information¹ and provides a corporate update
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoLeeds hospitals trust says finances are “critical” amid £110m deficit
-

 DeFi12 months ago
DeFi12 months ago🏴☠️ Pump.Fun operated by Insider Exploit
-

 Tech12 months ago
Tech12 months agoBitcoin’s Correlation With Tech Stocks Is At Its Highest Since August 2023: Bloomberg ⋆ ZyCrypto
-
 Tech12 months ago
Tech12 months agoEverything you need to know
-

 Markets11 months ago
Markets11 months agoWhale Investments in Bitcoin Hit $100 Billion in 2024, Fueling Insane Investor Optimism ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 News9 months ago
News9 months agoStocks wobble as Fed delivers and Meta bounces
-

 Videos12 months ago
Videos12 months ago“We will enter the ‘banana zone’ in 2 WEEKS! Cryptocurrency prices will quadruple!” – Raoul Pal